X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Arts syndrome, and prelingual non-syndromic deafness form a disease continuum: evidence from a family with a novel PRPS1 mutation
- PMID: 24528855
- PMCID: PMC3931488
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-9-24
X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Arts syndrome, and prelingual non-syndromic deafness form a disease continuum: evidence from a family with a novel PRPS1 mutation
Abstract
Background: X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 5 (CMTX5), Arts syndrome, and non-syndromic sensorineural deafness (DFN2) are allelic syndromes, caused by reduced activity of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase 1 (PRS-I) due to loss-of-function mutations in PRPS1. As only few families have been described, knowledge about the relation between these syndromes, the phenotypic spectrum in patients and female carriers, and the relation to underlying PRS-I activity is limited.
Methods: We investigated a family with a novel PRPS1 mutation (c.830A > C, p.Gln277Pro) by extensive phenotyping, MRI, and genetic and enzymatic tests.
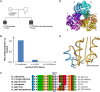
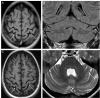
Results: The male index subject presented with an overlap of CMTX5 and Arts syndrome features, whereas his sister presented with prelingual DFN2. Both showed mild parietal and cerebellar atrophy on MRI. Enzymatically, PRS-I activity was undetectable in the index subject, reduced in his less affected sister, and normal in his unaffected mother.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that CMTX5, Arts syndrome and DFN2 are phenotypic clusters on an intrafamilial continuum, including overlapping phenotypes even within individuals. The respective phenotypic presentation seems to be determined by the exact PRPS1 mutation and the residual enzyme activity, the latter being largely influenced by the degree of skewed X-inactivation. Finally, our findings show that brain atrophy might be more common in PRPS1-disorders than previously thought.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expanding the phenotype of PRPS1 syndromes in females: neuropathy, hearing loss and retinopathy.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014 Dec 10;9:190. doi: 10.1186/s13023-014-0190-9. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014. PMID: 25491489 Free PMC article.
-
Association of PRPS1 Mutations with Disease Phenotypes.Dis Markers. 2015;2015:127013. doi: 10.1155/2015/127013. Epub 2015 May 24. Dis Markers. 2015. PMID: 26089585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expanding spectrum of PRPS1-associated phenotypes: three novel mutations segregating with X-linked hearing loss and mild peripheral neuropathy.Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 Jun;23(6):766-73. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.168. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25182139 Free PMC article.
-
X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 5 with recurrent weakness after febrile illness.Brain Dev. 2019 Feb;41(2):201-204. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2018.08.006. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Brain Dev. 2019. PMID: 30177296
-
Hearing loss and PRPS1 mutations: Wide spectrum of phenotypes and potential therapy.Int J Audiol. 2013 Jan;52(1):23-8. doi: 10.3109/14992027.2012.736032. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Int J Audiol. 2013. PMID: 23190330 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Additive reductions in zebrafish PRPS1 activity result in a spectrum of deficiencies modeling several human PRPS1-associated diseases.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 18;6:29946. doi: 10.1038/srep29946. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27425195 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothesis: evidence that the PRS gene products of Saccharomyces cerevisiae support both PRPP synthesis and maintenance of cell wall integrity.Curr Genet. 2024 May 11;70(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s00294-024-01290-w. Curr Genet. 2024. PMID: 38733432 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic characteristics of a patient with phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1 deficiency and a systematic literature review.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2023 Jun 19;36:100986. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2023.100986. eCollection 2023 Sep. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2023. PMID: 37670898 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the phenotype of PRPS1 syndromes in females: neuropathy, hearing loss and retinopathy.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014 Dec 10;9:190. doi: 10.1186/s13023-014-0190-9. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014. PMID: 25491489 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of X-Chromosome Inactivation on Phenotypic Expression of X-Linked Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Brain Sci. 2021 Jul 9;11(7):904. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11070904. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34356138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim JW, Kim HJ, In: GeneReviews. Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, editor. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993/2011. Charcot-Marie-Tooth Neuropathy X Type 5. Accessed on November 2nd, 2013.
-
- Kim HJ, Sohn KM, Shy ME. et al.Mutations in PRPS1, which encodes the phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase enzyme critical for nucleotide biosynthesis, cause hereditary peripheral neuropathy with hearing loss and optic neuropathy (cmtx5) Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81(3):552–558. doi: 10.1086/519529. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Brouwer APM, Duley JA, Christodoulou J, In: GeneReviews. Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, editor. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993/2011. Arts syndrome. Accessed on November 2nd, 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

