Applications of gold nanoparticles in cancer nanotechnology
- PMID: 24198458
- PMCID: PMC3808249
- DOI: 10.2147/nsa.s3788
Applications of gold nanoparticles in cancer nanotechnology
Abstract
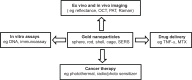
It has been almost 4 decades since the "war on cancer" was declared. It is now generally believed that personalized medicine is the future for cancer patient management. Possessing unprecedented potential for early detection, accurate diagnosis, and personalized treatment of cancer, nanoparticles have been extensively studied over the last decade. In this review, we will summarize the current state-of-the-art of gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications targeting cancer. Gold nanospheres, nanorods, nanoshells, nanocages, and surface enhanced Raman scattering nanoparticles will be discussed in detail regarding their uses in in vitro assays, ex vivo and in vivo imaging, cancer therapy, and drug delivery. Multifunctionality is the key feature of nanoparticle-based agents. Targeting ligands, imaging labels, therapeutic drugs, and other functionalities can all be integrated to allow for targeted molecular imaging and molecular therapy of cancer. Big strides have been made and many proof-of-principle studies have been successfully performed. The future looks brighter than ever yet many hurdles remain to be conquered. A multifunctional platform based on gold nanoparticles, with multiple receptor targeting, multimodality imaging, and multiple therapeutic entities, holds the promise for a "magic gold bullet" against cancer.
Keywords: cancer; gold nanoparticles; molecular therapy; nanomedicine; nanotechnology; optical imaging.
Figures

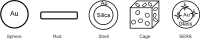

Similar articles
-
Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine.J Phys Chem B. 2006 Apr 13;110(14):7238-48. doi: 10.1021/jp057170o. J Phys Chem B. 2006. PMID: 16599493
-
Nanotechnology: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(19):1-43. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074489 Free PMC article.
-
Gold Fluorescence Nanoparticles for Enhanced SERS Detection in Biomedical Sensor Applications: Current Trends and Future Directions.Chem Rec. 2024 Feb 5:e202300303. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202300303. Online ahead of print. Chem Rec. 2024. PMID: 38314935 Review.
-
Gold Nanoparticles- Boon in Cancer Theranostics.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(40):5134-5151. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200701151403. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32611300 Review.
-
Nanoplatforms for targeted molecular imaging in living subjects.Small. 2007 Nov;3(11):1840-54. doi: 10.1002/smll.200700351. Small. 2007. PMID: 17943716 Review.
Cited by
-
The nano era in dentistry.J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2013 Jan;4(1):39-44. doi: 10.4103/0976-9668.107258. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23633833 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotechnology in diagnostics and therapeutics for gastrointestinal disorders.Dig Liver Dis. 2013 Dec;45(12):995-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.03.019. Epub 2013 May 7. Dig Liver Dis. 2013. PMID: 23660079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential of Nano-Based Photodynamic Treatment as a Therapy against Oral Leukoplakia: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 28;12(21):6819. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216819. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo and ex vivo applications of gold nanoparticles for biomedical SERS imagingi.Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;2(2):232-41. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 23133814 Free PMC article.
-
Photothermal therapy via a gold nanoparticle-coated stent for treating stent-induced granulation tissue formation in the rat esophagus.Sci Rep. 2021 May 18;11(1):10558. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90182-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34006988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal A, Huang S, Wei Haw Lin A, et al. Quantitative evaluation of optical coherence tomography signal enhancement with gold nanoshells. J Biomed Opt. 2006;11:041121. - PubMed
-
- Anshup A, Venkataraman JS, Subramaniam C, et al. Growth of gold nanoparticles in human cells. Langmuir. 2005;21:11562–7. - PubMed
-
- Bikram M, Gobin AM, Whitmire RE, et al. Temperature-sensitive hydrogels with SiO2-Au nanoshells for controlled drug delivery. J Control Release. 2007;123:219–27. - PubMed
-
- Bremer C, Tung CH, Weissleder R. In vivo molecular target assessment of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition. Nat Med. 2001;7:743–8. - PubMed
-
- Brust M, Walker M, Bethell D, et al. Synthesis of thiol-derivatized gold nanoparticles in a two-phase liquid-liquid system. J Chem Soc Chem Commun. 1994:801–2.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

