Hereditary spastic paraplegia type 43 (SPG43) is caused by mutation in C19orf12
- PMID: 23857908
- PMCID: PMC3819934
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.22378
Hereditary spastic paraplegia type 43 (SPG43) is caused by mutation in C19orf12
Abstract
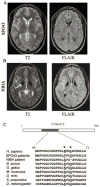
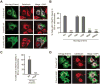
We report here the genetic basis for a form of progressive hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG43) previously described in two Malian sisters. Exome sequencing revealed a homozygous missense variant (c.187G>C; p.Ala63Pro) in C19orf12, a gene recently implicated in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA). The same mutation was subsequently also found in a Brazilian family with features of NBIA, and we identified another NBIA patient with a three-nucleotide deletion (c.197_199del; p.Gly66del). Haplotype analysis revealed that the p.Ala63Pro mutations have a common origin, but MRI scans showed no brain iron deposition in the Malian SPG43 subjects. Heterologous expression of these SPG43 and NBIA variants resulted in similar alterations in the subcellular distribution of C19orf12. The SPG43 and NBIA variants reported here as well as the most common C19orf12 missense mutation reported in NBIA patients are found within a highly conserved, extended hydrophobic domain in C19orf12, underscoring the functional importance of this domain.
Keywords: C19orf12; NBIA; SPG43; hereditary spastic paraplegia.
Published 2013. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. **This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutational analysis of the CYP7B1, PNPLA6 and C19orf12 genes in autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia.Mol Cell Probes. 2016 Feb;30(1):53-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 20. Mol Cell Probes. 2016. PMID: 26714052
-
Distal muscle weakness and optic atrophy without central nervous system involvement in a patient with a homozygous missense mutation in the C19ORF12-gene.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021 Jul;206:106637. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2021.106637. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34022688
-
C19orf12 mutation causing mitochondrial membrane-protein Associated Neurodegeneration masquerading as spastic paraplegia.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021 Aug;89:146-147. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2021.07.014. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 34298215
-
SPG43 and ALS-like syndrome in the same family due to compound heterozygous mutations of the C19orf12 gene: a case description and brief review.Neurogenetics. 2021 Mar;22(1):95-101. doi: 10.1007/s10048-020-00631-4. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Neurogenetics. 2021. PMID: 33394258 Review.
-
A novel homozygous variant in RNF170 causes hereditary spastic paraplegia: a case report and review of the literature.Neurogenetics. 2022 Apr;23(2):85-90. doi: 10.1007/s10048-022-00685-6. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Neurogenetics. 2022. PMID: 35041108 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and defects in lipid homeostasis as therapeutic targets in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation.Rare Dis. 2016 Jan 25;4(1):e1128616. doi: 10.1080/21675511.2015.1128616. eCollection 2016. Rare Dis. 2016. PMID: 27141409 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in Rare (NonLysosomal) Neurodegenerative Diseases.J Mol Biol. 2020 Apr 3;432(8):2735-2753. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.02.012. Epub 2020 Feb 19. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32087199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of lipids for upper motor neuron health and disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr;112:92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33323321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: Clinical and Genetic Hallmarks.Cerebellum. 2017 Apr;16(2):525-551. doi: 10.1007/s12311-016-0803-z. Cerebellum. 2017. PMID: 27271711 Review.
-
Insights into Clinical, Genetic, and Pathological Aspects of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegias: A Comprehensive Overview.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Nov 26;8:690899. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.690899. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34901147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deschauer M, Gaul C, Behrmann C, Prokisch H, Zierz S, Haack TB. C19orf12 mutations in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation mimicking juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol. 2012;259(11):2434–2439. - PubMed
-
- Erichsen AK, Koht J, Stray-Pedersen A, Abdelnoor M, Tallaksen CM. Prevalence of hereditary ataxia and spastic paraplegia in southeast Norway: a population-based study. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 6):1577–1588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZIA NR000026-02/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS054132/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS054132/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA NS002974-12/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS072248/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA NS002974/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 NR999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS069700/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS072248/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA HG000215/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA HG000215-10/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA NR000026-01/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- 1ZIA NS002974-13/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

