Allopurinol Use during Pregnancy - Outcome of 31 Prospectively Ascertained Cases and a Phenotype Possibly Indicative for Teratogenicity
- PMID: 23840514
- PMCID: PMC3686712
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066637
Allopurinol Use during Pregnancy - Outcome of 31 Prospectively Ascertained Cases and a Phenotype Possibly Indicative for Teratogenicity
Abstract
Allopurinol is a purine analogue that inhibits xanthine oxidase. It is mainly used for the treatment of hyperuricemia in patients with gout or tumor lysis syndrome. Experience with allopurinol in pregnancy is scarce. In 2011, Kozenko et al. reported on a child with multiple malformations after maternal treatment with allopurinol throughout pregnancy. Possible teratogenicity of allopurinol was proposed due to the similarity of the pattern of malformations in children with mycophenolate embryopathy. A possible common mechanism of both drugs, i.e. disruption of purine synthesis, was discussed. We report on the outcome of 31 prospectively ascertained pregnancies with allopurinol exposure at least during first trimester. Pregnancy outcomes were 2 spontaneous abortions, 2 elective terminations of pregnancy and 27 live born children. The overall rate of major malformations (3.7%) and of spontaneous abortions (cumulative incidence 11%, 95%-CI 3-40) were both within the normal range. However, there was one child with severe malformations including microphthalmia, cleft lip and palate, renal hypoplasia, low-set ears, hearing deficit, bilateral cryptorchidism, and micropenis. The striking similarity of the anomalies in this child and the case described by Kozenko et al. might be considered as a signal for teratogenicity. Thus, we would recommend caution with allopurinol treatment in the first trimester, until further data are available.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
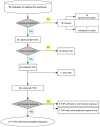
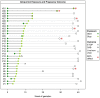
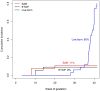
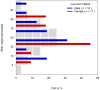
Similar articles
-
Teratogenicity of mycophenolate confirmed in a prospective study of the European Network of Teratology Information Services.Am J Med Genet A. 2012 Mar;158A(3):588-96. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35223. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Am J Med Genet A. 2012. PMID: 22319001
-
Potential teratogenic effects of allopurinol: a case report.Am J Med Genet A. 2011 Sep;155A(9):2247-52. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.34139. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Am J Med Genet A. 2011. PMID: 21815259
-
The teratogenicity of allopurinol: A comprehensive review of animal and human studies.Reprod Toxicol. 2018 Oct;81:180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Reprod Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30125681 Review.
-
Multicentre study and systematic review: Allopurinol exposure during pregnancy.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Aug;60(4):503-518. doi: 10.1111/apt.18126. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38984819
-
Rasburicase represents a new tool for hyperuricemia in tumor lysis syndrome and in gout.Int J Med Sci. 2007 Mar 2;4(2):83-93. doi: 10.7150/ijms.4.83. Int J Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 17396159 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Xanthine Oxidase in Pregnancy Complications: A Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 14;13(10):1234. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101234. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A best practice position statement on pregnancy in chronic kidney disease: the Italian Study Group on Kidney and Pregnancy.J Nephrol. 2016 Jun;29(3):277-303. doi: 10.1007/s40620-016-0285-6. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26988973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urate-lowering agents do not have clinically relevant negative effects on sperm quality and reproductive hormones in men with gout: a prospective open-label cohort study.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Jul;44(7):1245-1253. doi: 10.1007/s00296-024-05572-x. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38538820 Clinical Trial.
-
The first review on prenatal drug exposure and ocular malformation occurrence.Front Pediatr. 2024 Sep 4;12:1379875. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1379875. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39296666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IBD: reproductive health, pregnancy and lactation.Frontline Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan;6(1):38-43. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2014-100430. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 28839793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Struthers A, Shearer F (2012) Allopurinol: novel indications in cardiovascular disease. Heart 98: 1543–1545 heartjnl-2012-302249 [pii];10.1136/heartjnl-2012-302249 [doi] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miller SL, Wallace EM, Walker DW (2012) Antioxidant therapies: a potential role in perinatal medicine. Neuroendocrinology 96: 13–23 000336378 [pii];10.1159/000336378 [doi] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hoentjen F, Seinen ML, Hanauer SB, de Boer NK, Rubin DT, et al... (2012) Safety and effectiveness of long-term allopurinol-thiopurine maintenance treatment in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 10.1002/ibd.23021 [doi]. - PubMed
-
- Seinen ML, de Boer NK, Smid K, van Asseldonk DP, Bouma G, et al. (2011) Allopurinol enhances the activity of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase in inflammatory bowel disease patients during low-dose thiopurine therapy: preliminary data of an ongoing series. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 30: 1085–1090 10.1080/15257770.2011.597371 [doi] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seinen ML, de Boer NK, van Hoorn ME, van Bodegraven AA, Bouma G (2012) Safe use of allopurinol and low-dose mercaptopurine therapy during pregnancy in an ulcerative colitis patient. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 10.1002/ibd.22945 [doi]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

