Influence of implantation age on school-age language performance in pediatric cochlear implant users
- PMID: 23448124
- PMCID: PMC3742378
- DOI: 10.3109/14992027.2012.759666
Influence of implantation age on school-age language performance in pediatric cochlear implant users
Abstract
Objective: This study examined specific spoken language abilities of 160 children with severe-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss followed prospectively 4, 5, or 6 years after cochlear implantation.
Study sample: Ninety-eight children received implants before 2.5 years, and 62 children received implants between 2.5 and 5 years of age.
Design: Language was assessed using four subtests of the Comprehensive Assessment of Spoken Language (CASL). Standard scores were evaluated by contrasting age of implantation and follow-up test time.
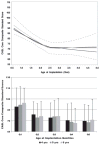
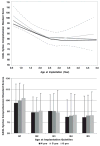
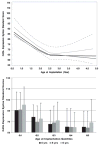
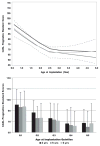
Results: Children implanted under 2.5 years of age achieved higher standard scores than children with older ages of implantation for expressive vocabulary, expressive syntax, and pragmatic judgments. However, in both groups, some children performed more than two standard deviations below the standardization group mean, while some scored at or well above the mean.
Conclusions: Younger ages of implantation are associated with higher levels of performance, while later ages of implantation are associated with higher probabilities of continued language delays, particularly within subdomains of grammar and pragmatics. Longitudinal data from this cohort study demonstrate that after 6 years of implant experience, there is large variability in language outcomes associated with modifiers of rates of language learning that differ as children with implants age.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of early auditory experience on the spoken language of deaf children at 3 years of age.Ear Hear. 2006 Jun;27(3):286-98. doi: 10.1097/01.aud.0000215973.76912.c6. Ear Hear. 2006. PMID: 16672797 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-based guidelines for recommending cochlear implantation for young children: Audiological criteria and optimizing age at implantation.Int J Audiol. 2016;55 Suppl 2:S9-S18. doi: 10.3109/14992027.2016.1157268. Epub 2016 May 4. Int J Audiol. 2016. PMID: 27142630
-
Typical consonant cluster acquisition in auditory-verbal children with early-identified severe/profound hearing loss.Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2014 Feb;16(1):69-81. doi: 10.3109/17549507.2013.808698. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24001172
-
Does cochlear implantation improve speech recognition in children with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder? A systematic review.Int J Audiol. 2013 Jul;52(7):442-54. doi: 10.3109/14992027.2013.786190. Epub 2013 May 24. Int J Audiol. 2013. PMID: 23705807 Review.
-
Predicting the Future: A Case Study in Prognostication.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2017 Nov 8;26(4):1057-1065. doi: 10.1044/2017_AJSLP-17-0022. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28973121 Review.
Cited by
-
Les effets sur le langage d’une implantation cochléaire.Can Fam Physician. 2022 Oct;68(10):739-741. doi: 10.46747/cfp.6810739. Can Fam Physician. 2022. PMID: 36241407 Free PMC article. French.
-
Consonant and Vowel Confusions in Well-Performing Children and Adolescents With Cochlear Implants, Measured by a Nonsense Syllable Repetition Test.Front Psychol. 2019 Aug 14;10:1813. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01813. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31474900 Free PMC article.
-
Language evaluation in children with pre-lingual hearing loss and cochlear implant.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Jan-Feb;86(1):91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 30527397 Free PMC article.
-
A Modified Pediatric Ranked Order Speech Perception Score to Assess Speech Recognition Development in Children With Cochlear Implants.Am J Audiol. 2022 Sep;31(3):613-632. doi: 10.1044/2022_AJA-21-00212. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Am J Audiol. 2022. PMID: 35767328 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Effectiveness of Cochlear Implantation of Young Children, Including Those With Complicating Conditions.Otol Neurotol. 2019 Apr;40(4):454-463. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002156. Otol Neurotol. 2019. PMID: 30870355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archbold S, Harris M, O’Donoghue G, Nikolopoulos T, White A, et al. Reading abilities after cochlear implantation: The effect of age at implantation on outcomes at 5 and 7 years after implantation. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;72:1471–1478. - PubMed
-
- Bates E, Thal D, Finlay B, Clancy B. Early language development and its neural correlates. In: Segalowitz S, Rapin I, editors. Handbook of Neuropsychology. 2. New York: Elsevier; 2003. pp. 525–592. Part II. Child Neuropsychology.
-
- Bayley N. Bayley Scales of Infant Development. 2. San Antonio, USA: The Psychological Corporation; 1993.
-
- Carrow-Woolfolk E. Comprehensive Assessment of Spoken Language. San Antonio, USA: American Guidance Services; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
