Sticking together: building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way
- PMID: 23353768
- PMCID: PMC3936787
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2960
Sticking together: building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way
Abstract
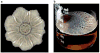
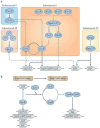
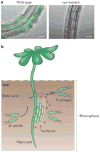
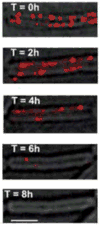
Biofilms are ubiquitous communities of tightly associated bacteria encased in an extracellular matrix. Bacillus subtilis has long served as a robust model organism to examine the molecular mechanisms of biofilm formation, and a number of studies have revealed that this process is regulated by several integrated pathways. In this Review, we focus on the molecular mechanisms that control B. subtilis biofilm assembly, and then briefly summarize the current state of knowledge regarding biofilm disassembly. We also discuss recent progress that has expanded our understanding of B. subtilis biofilm formation on plant roots, which are a natural habitat for this soil bacterium.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cyclic di-AMP Acts as an Extracellular Signal That Impacts Bacillus subtilis Biofilm Formation and Plant Attachment.mBio. 2018 Mar 27;9(2):e00341-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00341-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29588402 Free PMC article.
-
Biocontrol of Bacillus subtilis against infection of Arabidopsis roots by Pseudomonas syringae is facilitated by biofilm formation and surfactin production.Plant Physiol. 2004 Jan;134(1):307-19. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.028712. Epub 2003 Dec 18. Plant Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14684838 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis: new insights into regulatory strategies and assembly mechanisms.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Aug;93(4):587-98. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12697. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24988880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biofilm Formation Drives Transfer of the Conjugative Element ICEBs1 in Bacillus subtilis.mSphere. 2018 Sep 26;3(5):e00473-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00473-18. mSphere. 2018. PMID: 30258041 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis biofilm formation and social interactions.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021 Sep;19(9):600-614. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00540-9. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33824496 Review.
Cited by
-
Response and Adaptation of Microbial Community in a CANON Reactor Exposed to an Extreme Alkaline Shock.Archaea. 2020 Jun 23;2020:8888615. doi: 10.1155/2020/8888615. eCollection 2020. Archaea. 2020. PMID: 32694931 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a Novel Multi-Strains Probiotic Formulation with Improved Efficacy toward Intestinal Inflammation.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 30;12(7):1945. doi: 10.3390/nu12071945. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32629887 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of Candida albicans Biofilms.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Jun 1;80(3):565-95. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00068-15. Print 2016 Sep. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27250770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thio Derivatives of 2(5H)-Furanone as Inhibitors against Bacillus subtilis Biofilms.Acta Naturae. 2015 Apr-Jun;7(2):102-7. Acta Naturae. 2015. PMID: 26085951 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience in the Face of Uncertainty: Sigma Factor B Fine-Tunes Gene Expression To Support Homeostasis in Gram-Positive Bacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Jul 15;82(15):4456-4469. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00714-16. Print 2016 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27208112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cohn F. Untersuchungen über bacterien. IV. Beiträge zur biologie der Bacillen. Beiträge zur biologie der Pflanzen. 1877;7:249–276.
-
- Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:95–108. - PubMed
-
- Stewart PS, Franklin MJ. Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:199–210. - PubMed
-
- Davies D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:114–122. - PubMed
-
- Mah TF, O’Toole GA. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9:34–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

