DNA helicases associated with genetic instability, cancer, and aging
- PMID: 23161009
- PMCID: PMC4538701
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5037-5_6
DNA helicases associated with genetic instability, cancer, and aging
Abstract
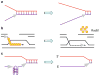
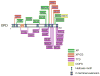
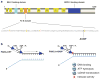
DNA helicases have essential roles in the maintenance of genomic -stability. They have achieved even greater prominence with the discovery that mutations in human helicase genes are responsible for a variety of genetic disorders and are associated with tumorigenesis. A number of missense mutations in human helicase genes are linked to chromosomal instability diseases characterized by age-related disease or associated with cancer, providing incentive for the characterization of molecular defects underlying aberrant cellular phenotypes. In this chapter, we discuss some examples of clinically relevant missense mutations in various human DNA helicases, particularly those of the Iron-Sulfur cluster and RecQ families. Clinically relevant mutations in the XPD helicase can lead to Xeroderma pigmentosum, Cockayne's syndrome, Trichothiodystrophy, or COFS syndrome. FANCJ mutations are associated with Fanconi anemia or breast cancer. Mutations of the Fe-S helicase ChlR1 (DDX11) are linked to Warsaw Breakage syndrome. Mutations in the RecQ helicases BLM and WRN are linked to the cancer-prone disorder Bloom's syndrome and premature aging condition Werner syndrome, respectively. RECQL4 mutations can lead to Rothmund-Thomson syndrome, Baller-Gerold syndrome, or RAPADILINO. Mutations in the Twinkle mitochondrial helicase are responsible for several neuromuscular degenerative disorders. We will discuss some insights gained from biochemical and genetic studies of helicase variants, and highlight some hot areas of helicase research based on recent developments.
Figures
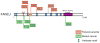

Similar articles
-
Disease-causing missense mutations in human DNA helicase disorders.Mutat Res. 2013 Apr-Jun;752(2):138-152. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2012.12.004. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23276657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human RecQL4 helicase plays multifaceted roles in the genomic stability of normal and cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2018 Jan 28;413:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 29080750 Review.
-
DNA helicases, genomic instability, and human genetic disease.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2000;1:409-59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.1.1.409. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 11701636 Review.
-
Human RecQ Helicases in DNA Double-Strand Break Repair.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 25;9:640755. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.640755. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33718381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bloom's syndrome: Why not premature aging?: A comparison of the BLM and WRN helicases.Ageing Res Rev. 2017 Jan;33:36-51. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 26. Ageing Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 27238185 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An E2F1/DDX11/EZH2 Positive Feedback Loop Promotes Cell Proliferation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 5;10:593293. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.593293. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33614480 Free PMC article.
-
Multigene panel testing beyond BRCA1/2 in breast/ovarian cancer Spanish families and clinical actionability of findings.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Dec;144(12):2495-2513. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2763-9. Epub 2018 Oct 10. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30306255
-
A synopsis on aging-Theories, mechanisms and future prospects.Ageing Res Rev. 2016 Aug;29:90-112. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Ageing Res Rev. 2016. PMID: 27353257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory stress and sarcomagenesis: a vicious interplay.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014 Jan;19(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s12192-013-0449-4. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014. PMID: 24046208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Checkpoint-dependent and independent roles of the Werner syndrome protein in preserving genome integrity in response to mild replication stress.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Nov 10;42(20):12628-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1022. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25352544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lohman TM, Tomko EJ, Wu CG. Non-hexameric DNA helicases and translocases: mechanisms and regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Singleton MR, Dillingham MS, Wigley DB. Structure and mechanism of helicases and nucleic acid translocases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:23–50. - PubMed
-
- Lohman TM, Bjornson KP. Mechanisms of helicase-catalyzed DNA unwinding. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:169–214. - PubMed
-
- Patel SS, Donmez I. Mechanisms of helicases. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:18265–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

