BAP1 cancer syndrome: malignant mesothelioma, uveal and cutaneous melanoma, and MBAITs
- PMID: 22935333
- PMCID: PMC3493315
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-179
BAP1 cancer syndrome: malignant mesothelioma, uveal and cutaneous melanoma, and MBAITs
Abstract
Background: BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1) is a tumor suppressor gene located on chromosome 3p21. Germline BAP1 mutations have been recently associated with an increased risk of malignant mesothelioma, atypical melanocytic tumors and other neoplasms. To answer the question if different germline BAP1 mutations may predispose to a single syndrome with a wide phenotypic range or to distinct syndromes, we investigated the presence of melanocytic tumors in two unrelated families (L and W) with germline BAP1 mutations and increased risk of malignant mesothelioma.
Methods: Suspicious cutaneous lesions were clinically and pathologically characterized and compared to those present in other families carrying BAP1 mutations. We then conducted a meta-analysis of all the studies reporting BAP1-mutated families to survey cancer risk related to the germline BAP1 mutation (means were compared using t-test and proportions were compared with Pearson χ2 test or two-tailed Fisher's exact test).
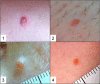
Results: Melanocytic tumors: of the five members of the L family studied, four (80%) carried a germline BAP1 mutation (p.Gln684*) and also presented one or more atypical melanocytic tumors; of the seven members of W family studied, all carried a germline BAP1 mutation (p.Pro147fs*48) and four of them (57%) presented one or more atypical melanocytic tumors, that we propose to call "melanocytic BAP1-mutated atypical intradermal tumors" (MBAITs). Meta-analysis: 118 individuals from seven unrelated families were selected and divided into a BAP1-mutated cohort and a BAP1-non-mutated cohort. Malignant mesothelioma, uveal melanoma, cutaneous melanoma, and MBAITs prevalence was significantly higher in the BAP1-mutated cohort (p ≤ 0.001).
Conclusions: Germline BAP1 mutations are associated with a novel cancer syndrome characterized by malignant mesothelioma, uveal melanoma, cutaneous melanoma and MBAITs, and possibly by other cancers. MBAITs provide physicians with a marker to identify individuals who may carry germline BAP1 mutations and thus are at high risk of developing associated cancers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genotypic and Phenotypic Features of BAP1 Cancer Syndrome: A Report of 8 New Families and Review of Cases in the Literature.JAMA Dermatol. 2017 Oct 1;153(10):999-1006. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.2330. JAMA Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28793149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BAP1 Syndrome - Predisposition to Malignant Mesothelioma, Skin and Uveal Melanoma, Renal and Other Cancers.Klin Onkol. 2019 Summer;32(Supplementum2):118-122. doi: 10.14735/amko2019S118. Klin Onkol. 2019. PMID: 31409087 English.
-
[Malignant mesothelioma and constitutional BAP1 gene mutations].Rev Mal Respir. 2019 Feb;36(2):241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2017.11.014. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Rev Mal Respir. 2019. PMID: 30686559 Review. French.
-
Comparison of Germline versus Somatic BAP1 Mutations for Risk of Metastasis in Uveal Melanoma.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 26;18(1):1172. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5079-x. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30477459 Free PMC article.
-
Germline BAP1 mutations predispose to malignant mesothelioma.Nat Genet. 2011 Aug 28;43(10):1022-5. doi: 10.1038/ng.912. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 21874000 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Melanoma epidemiology, biology and prognosis.EJC Suppl. 2013 Sep;11(2):81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcsup.2013.07.012. EJC Suppl. 2013. PMID: 26217116 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Genomics and Functional Genomics of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 1;21(17):6342. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176342. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32882916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of H2A ubiquitination and SLC7A11 expression by BAP1 and PRC1.Cell Cycle. 2019 Apr;18(8):773-783. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1597506. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 30907299 Free PMC article.
-
How to Better Understand the Influence of Host Genetics on Developing an Effective Immune Response to Thoracic Cancers.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 21;11:679609. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.679609. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34235080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Molecular Pathways in Melanomagenesis: Characterization of Therapeutic Targets.Front Oncol. 2015 Aug 10;5:183. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00183. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26322273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jensen DE, Proctor M, Marquis ST, Gardner HP, Ha SI, Chodosh LA, Ishov AM, Tommerup N, Vissing H, Sekido Y, Minna J, Borodovsky A, Schultz DC, Wilkinson KD, Maul GG, Barlev N, Berger SL, Prendergast GC, Rauscher FJ 3rd. BAP1: a novel ubiquitin hydrolase which binds to the BRCA1 RING finger and enhances BRCA1-mediated cell growth suppression. Oncogene. 1998;16(9):1097–1112. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201861. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu H, Mashtalir N, Daou S, Hammond-Martel I, Ross J, Sui G, Hart GW, 3rd Rauscher FJ, Drobetsky E, Milot E, Shi Y, Affar el B. The ubiquitin carboxyl hydrolase BAP1 forms a ternary complex with YY1 and HCF-1 and is a critical regulator of gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(21):5071–5085. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00396-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

