MRI characteristics and scoring in HDLS due to CSF1R gene mutations
- PMID: 22843259
- PMCID: PMC3413763
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318263575a
MRI characteristics and scoring in HDLS due to CSF1R gene mutations
Abstract
Objective: To describe the brain MRI characteristics of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids (HDLS) with known mutations in the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor gene (CSF1R) on chromosome 5.
Methods: We reviewed 20 brain MRI scans of 15 patients with autopsy- or biopsy-verified HDLS and CSF1R mutations. We assessed sagittal T1-, axial T1-, T2-, proton density-weighted and axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images for distribution of white matter lesions (WMLs), gray matter involvement, and atrophy. We calculated a severity score based on a point system (0-57) for each MRI scan.
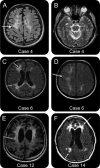
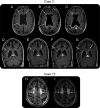
Results: Of the patients, 93% (14 of 15) demonstrated localized WMLs with deep and subcortical involvement, whereas one patient revealed generalized WMLs. All WMLs were bilateral but asymmetric and predominantly frontal. Fourteen patients had a rapidly progressive clinical course with an initial MRI mean total severity score of 16.7 points (range 10-33.5). Gray matter pathology and brainstem atrophy were absent, and the corticospinal tracts were involved late in the disease course. There was no enhancement, and there was minimal cerebellar pathology.
Conclusion: Recognition of the typical MRI patterns of HDLS and the use of an MRI severity score might help during the diagnostic evaluation to characterize the natural history and to monitor potential future treatments. Indicators of rapid disease progression were symptomatic disease onset before 45 years, female sex, WMLs extending beyond the frontal regions, a MRI severity score greater than 15 points, and mutation type of deletion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discriminative clinical and neuroimaging features of motor-predominant hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and primary progressive multiple sclerosis: A preliminary cross-sectional study.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019 Jun;31:22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2019.03.008. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 30901701
-
Imaging features in conventional MRI, spectroscopy and diffusion weighted images of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids (HDLS).J Neurol. 2014 Dec;261(12):2351-9. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7509-2. Epub 2014 Sep 20. J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25239393
-
Parkinsonian features in hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids (HDLS) and CSF1R mutations.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013 Oct;19(10):869-77. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.05.013. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013. PMID: 23787135 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical and neuroimaging characteristics of patients with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids (HDLS)].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014;54(12):1158-61. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.54.1158. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014. PMID: 25519969 Review. Japanese.
-
[Neuropathology of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids (HDLS)].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014;54(12):1165-7. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.54.1165. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014. PMID: 25672734 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles for CSF-1 Receptor and its Ligands in the Nervous System.Trends Neurosci. 2016 Jun;39(6):378-393. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Trends Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27083478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel A781V mutation in the CSF1R gene causes hereditary diffuse leucoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Sep 15;332(1-2):141-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23816250 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of Brain Calcifications in Adult-Onset Leukoencephalopathy with Axonal Spheroids and Pigmented Glia.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Jan;38(1):77-83. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4938. Epub 2016 Sep 15. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 27633805 Free PMC article.
-
[Hereditary diffuse leukencephalopathy with spheroids: a microgliopathy due to CSF1 receptor impairment].Nervenarzt. 2014 Apr;85(4):465-70. doi: 10.1007/s00115-014-4052-4. Nervenarzt. 2014. PMID: 24706185 German.
-
Intrafamilial heterogeneity in hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids.Neurol Clin Pract. 2019 Dec;9(6):500-502. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000647. Neurol Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 32042490 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- van der Knaap M, Valk J, Barkhof F, eds. Magnetic Resonance of Myelination and Myelin Disorders, 3rd ed New York: Birkhäuser; 2005
-
- Axelsson R, Roytta M, Sourander P, Akesson HO, Andersen O. Hereditary diffuse leucoencephalopathy with spheroids. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 1984;314:1–65 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
