Association of UBQLN1 mutation with Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome but not typical ALS
- PMID: 22766032
- PMCID: PMC4245016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.06.018
Association of UBQLN1 mutation with Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome but not typical ALS
Abstract
Genetic variants in UBQLN1 gene have been linked to neurodegeneration and mutations in UBQLN2 have recently been identified as a rare cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Objective: To test if genetic variants in UBQLN1 are involved in ALS.
Methods: 102 and 94 unrelated patients with familial and sporadic forms of ALS were screened for UBQLN1 gene mutations. Single nucleotide variants were further screened in a larger set of sporadic ALS (SALS) patients and unrelated control subjects using high-throughput Taqman genotyping; variants were further assessed for novelty using the 1000Genomes and NHLBI databases. In vitro studies tested the effect of UBQLN1 variants on the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS).
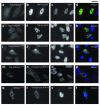
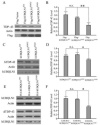
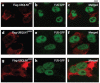
Results: Only two UBQLN1 coding variants were detected in the familial and sporadic ALS DNA set; one, the missense mutation p.E54D, was identified in a single patient with atypical motor neuron disease consistent with Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome (BVVLS), for whom c20orf54 mutations had been excluded. Functional studies revealed that UBQLN1E54D protein forms cytosolic aggregates that contain mislocalized TDP-43 and impairs degradation of ubiquitinated proteins through the proteasome.
Conclusions: Genetic variants in UBQLN1 are not commonly associated with ALS. A novel UBQLN1 mutation (E45D) detected in a patient with BVVLS altered nuclear TDP-43 localization in vitro, suggesting that UPS dysfunction may also underlie the pathogenesis of this condition.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutation screening of SLC52A3, C19orf12, and TARDBP in Iranian ALS patients.Neurobiol Aging. 2019 Mar;75:225.e9-225.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.11.003. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Neurobiol Aging. 2019. PMID: 30553531
-
Exome sequencing reveals riboflavin transporter mutations as a cause of motor neuron disease.Brain. 2012 Sep;135(Pt 9):2875-82. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws161. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Brain. 2012. PMID: 22740598 Free PMC article.
-
Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome: a riboflavin-unresponsive patient with a novel mutation in the C20orf54 gene.Pediatr Neurol. 2012 Jun;46(6):407-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2012.03.008. Pediatr Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22633641
-
Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere Syndrome as a Mimic of Neuroimmune Disorders: 3 Cases From the Clinic and Review of the Literature.J Child Neurol. 2017 May;32(6):528-532. doi: 10.1177/0883073816689517. Epub 2017 Jan 24. J Child Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28116953 Review.
-
Key role of UBQLN2 in pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019 Jul 18;7(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0758-7. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31319884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling Neurodegenerative Disorders in Drosophila melanogaster.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 26;21(9):3055. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093055. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32357532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inherited Paediatric Motor Neuron Disorders: Beyond Spinal Muscular Atrophy.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:6509493. doi: 10.1155/2017/6509493. Epub 2017 May 28. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 28634552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel ALS-associated variant in UBQLN4 regulates motor axon morphogenesis.Elife. 2017 May 2;6:e25453. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25453. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28463112 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging mechanisms of molecular pathology in ALS.J Clin Invest. 2015 May;125(5):1767-79. doi: 10.1172/JCI71601. Epub 2015 May 1. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25932674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signature changes in ubiquilin expression in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington's disease.Brain Res. 2015 Feb 9;1597:37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.008. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25511991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bensemain F, Chapuis J, Tian J, Shi J, Thaker U, Lendon C, et al. Association study of the Ubiquilin gene with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;22(3):691–3. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, Hiltunen M, Parkinson M, Ingelsson M, Lange C, Ramasamy K, et al. Family-based association between Alzheimer’s disease and variants in UBQLN1. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(9):884–94. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, McQueen MB, Mullin K, Blacker D, Tanzi RE. Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nat Genet. 2007;39(1):17–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

