What lies behind the wish to hasten death? A systematic review and meta-ethnography from the perspective of patients
- PMID: 22606338
- PMCID: PMC3351420
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037117
What lies behind the wish to hasten death? A systematic review and meta-ethnography from the perspective of patients
Abstract
Background: There is a need for an in-depth approach to the meaning of the wish to hasten death (WTHD). This study aims to understand the experience of patients with serious or incurable illness who express such a wish.
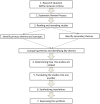
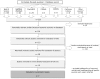
Methods and findings: Systematic review and meta-ethnography of qualitative studies from the patient's perspective. Studies were identified through six databases (ISI, PubMed, PsycINFO, CINAHL, CUIDEN and the Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials), together with citation searches and consultation with experts. Finally, seven studies reporting the experiences of 155 patients were included. The seven-stage Noblit and Hare approach was applied, using reciprocal translation and line-of-argument synthesis. Six main themes emerged giving meaning to the WTHD: WTHD in response to physical/psychological/spiritual suffering, loss of self, fear of dying, the desire to live but not in this way, WTHD as a way of ending suffering, and WTHD as a kind of control over one's life ('having an ace up one's sleeve just in case'). An explanatory model was developed which showed the WTHD to be a reactive phenomenon: a response to multidimensional suffering, rather than only one aspect of the despair that may accompany this suffering. According to this model the factors that lead to the emergence of WTHD are total suffering, loss of self and fear, which together produce an overwhelming emotional distress that generates the WTHD as a way out, i.e. to cease living in this way and to put an end to suffering while maintaining some control over the situation.
Conclusions: The expression of the WTHD in these patients is a response to overwhelming emotional distress and has different meanings, which do not necessarily imply a genuine wish to hasten one's death. These meanings, which have a causal relationship to the phenomenon, should be taken into account when drawing up care plans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding patients' experiences of the wish to hasten death: an updated and expanded systematic review and meta-ethnography.BMJ Open. 2017 Sep 29;7(9):e016659. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016659. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28965095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
A Blog-Based Study of Autistic Adults' Experiences of Aloneness and Connection and the Interplay with Well-Being: Corpus-Based and Thematic Analyses.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):437-449. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0073. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116056 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Qualitative study on perceived dignity of cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in China.Support Care Cancer. 2020 Jun;28(6):2921-2929. doi: 10.1007/s00520-019-05123-2. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Support Care Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31768731
-
The wish to die and hastening death in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A scoping review.BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2021 Sep;11(3):271-287. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2020-002640. Epub 2021 Jan 4. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2021. PMID: 33397660 Free PMC article.
-
Facing a request for assisted death - views of Finnish physicians, a mixed method study.BMC Med Ethics. 2024 May 3;25(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12910-024-01051-x. BMC Med Ethics. 2024. PMID: 38702731 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a short form of the Spanish schedule of attitudes toward hastened death in a palliative care population.Qual Life Res. 2017 Jan;26(1):235-239. doi: 10.1007/s11136-016-1409-0. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Qual Life Res. 2017. PMID: 27671489 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding patients' experiences of the wish to hasten death: an updated and expanded systematic review and meta-ethnography.BMJ Open. 2017 Sep 29;7(9):e016659. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016659. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28965095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnold EM. Factors that influence consideration of hastening death among people with life-threatening illnesses. Health & Social Work. 2004;29:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Grzybowska P, Finlay I. The incidence of suicide in palliative care patients. Palliative Medicine. 1997;11:313–316. - PubMed
-
- Hudson PL, Kristjanson LJ, Ashby M, Kelly B, Schofield P, et al. Desire for hastened death in patients with advanced disease and the evidence base of clinical guidelines: a systematic review. Palliative Medicine. 2006;20:693–701. - PubMed
-
- Lynn J. Learning to care for people with chronic illness facing the end of life. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2000;284:2508–2511. - PubMed
-
- Carmel S. The will to live: gender differences among elderly persons. Social Science & Medicine. 2001;52:949–958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous