Haploinsufficiency of ARID1B, a member of the SWI/SNF-a chromatin-remodeling complex, is a frequent cause of intellectual disability
- PMID: 22405089
- PMCID: PMC3309205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.007
Haploinsufficiency of ARID1B, a member of the SWI/SNF-a chromatin-remodeling complex, is a frequent cause of intellectual disability
Abstract
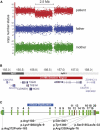
Intellectual disability (ID) is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous common condition that remains etiologically unresolved in the majority of cases. Although several hundred diseased genes have been identified in X-linked, autosomal-recessive, or syndromic types of ID, the establishment of an etiological basis remains a difficult task in unspecific, sporadic cases. Just recently, de novo mutations in SYNGAP1, STXBP1, MEF2C, and GRIN2B were reported as relatively common causes of ID in such individuals. On the basis of a patient with severe ID and a 2.5 Mb microdeletion including ARID1B in chromosomal region 6q25, we performed mutational analysis in 887 unselected patients with unexplained ID. In this cohort, we found eight (0.9%) additional de novo nonsense or frameshift mutations predicted to cause haploinsufficiency. Our findings indicate that haploinsufficiency of ARID1B, a member of the SWI/SNF-A chromatin-remodeling complex, is a common cause of ID, and they add to the growing evidence that chromatin-remodeling defects are an important contributor to neurodevelopmental disorders.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
BCL11A Haploinsufficiency Causes an Intellectual Disability Syndrome and Dysregulates Transcription.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Aug 4;99(2):253-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.05.030. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27453576 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical correlations of mutations affecting six components of the SWI/SNF complex: detailed description of 21 patients and a review of the literature.Am J Med Genet A. 2013 Jun;161A(6):1221-37. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35933. Epub 2013 May 1. Am J Med Genet A. 2013. PMID: 23637025 Review.
-
Mutations in SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex gene ARID1B cause Coffin-Siris syndrome.Nat Genet. 2012 Mar 18;44(4):379-80. doi: 10.1038/ng.2217. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 22426309
-
Expanding the phenotypic spectrum of ARID1B-mediated disorders and identification of altered cell-cycle dynamics due to ARID1B haploinsufficiency.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014 Mar 27;9:43. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-9-43. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014. PMID: 24674232 Free PMC article.
-
SWI/SNF complex in disorder: SWItching from malignancies to intellectual disability.Epigenetics. 2012 Nov;7(11):1219-24. doi: 10.4161/epi.22299. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Epigenetics. 2012. PMID: 23010866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BCL11A Haploinsufficiency Causes an Intellectual Disability Syndrome and Dysregulates Transcription.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Aug 4;99(2):253-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.05.030. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27453576 Free PMC article.
-
HSA21 Single-Minded 2 (Sim2) Binding Sites Co-Localize with Super-Enhancers and Pioneer Transcription Factors in Pluripotent Mouse ES Cells.PLoS One. 2015 May 8;10(5):e0126475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126475. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25955728 Free PMC article.
-
Brief Report: SETD2 Mutation in a Child with Autism, Intellectual Disabilities and Epilepsy.J Autism Dev Disord. 2015 Nov;45(11):3764-70. doi: 10.1007/s10803-015-2484-8. J Autism Dev Disord. 2015. PMID: 26084711
-
Inability to switch from ARID1A-BAF to ARID1B-BAF impairs exit from pluripotency and commitment towards neural crest formation in ARID1B-related neurodevelopmental disorders.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 9;12(1):6469. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26810-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34753942 Free PMC article.
-
High frequency strand slippage mutations in CTCF in MSI-positive endometrial cancers.Hum Mutat. 2014 Jan;35(1):63-5. doi: 10.1002/humu.22463. Hum Mutat. 2014. PMID: 24130125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ropers H.H. Genetics of early onset cognitive impairment. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2010;11:161–187. - PubMed
-
- Abou Jamra R., Philippe O., Raas-Rothschild A., Eck S.H., Graf E., Buchert R., Borck G., Ekici A., Brockschmidt F.F., Nöthen M.M. Adaptor protein complex 4 deficiency causes severe autosomal-recessive intellectual disability, progressive spastic paraplegia, shy character, and short stature. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011;88:788–795. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Najmabadi H., Hu H., Garshasbi M., Zemojtel T., Abedini S.S., Chen W., Hosseini M., Behjati F., Haas S., Jamali P. Deep sequencing reveals 50 novel genes for recessive cognitive disorders. Nature. 2011;478:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Endele S., Rosenberger G., Geider K., Popp B., Tamer C., Stefanova I., Milh M., Kortüm F., Fritsch A., Pientka F.K. Mutations in GRIN2A and GRIN2B encoding regulatory subunits of NMDA receptors cause variable neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:1021–1026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

