A congenital muscular dystrophy with mitochondrial structural abnormalities caused by defective de novo phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis
- PMID: 21665002
- PMCID: PMC3113344
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.05.010
A congenital muscular dystrophy with mitochondrial structural abnormalities caused by defective de novo phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis
Abstract
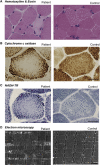
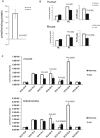
Congenital muscular dystrophy is a heterogeneous group of inherited muscle diseases characterized clinically by muscle weakness and hypotonia in early infancy. A number of genes harboring causative mutations have been identified, but several cases of congenital muscular dystrophy remain molecularly unresolved. We examined 15 individuals with a congenital muscular dystrophy characterized by early-onset muscle wasting, mental retardation, and peculiar enlarged mitochondria that are prevalent toward the periphery of the fibers but are sparse in the center on muscle biopsy, and we have identified homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in the gene encoding choline kinase beta (CHKB). This is the first enzymatic step in a biosynthetic pathway for phosphatidylcholine, the most abundant phospholipid in eukaryotes. In muscle of three affected individuals with nonsense mutations, choline kinase activities were undetectable, and phosphatidylcholine levels were decreased. We identified the human disease caused by disruption of a phospholipid de novo biosynthetic pathway, demonstrating the pivotal role of phosphatidylcholine in muscle and brain.
Copyright © 2011 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[New congenital muscular dystrophy due to CHKB mutations].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2013;53(11):1112-3. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.53.1112. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2013. PMID: 24291895 Review. Japanese.
-
Megaconial congenital muscular dystrophy due to loss-of-function mutations in choline kinase β.Curr Opin Neurol. 2013 Oct;26(5):536-43. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e328364c82d. Curr Opin Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23945283 Review.
-
Alteration of mitochondrial membrane inner potential in three Italian patients with megaconial congenital muscular dystrophy carrying new mutations in CHKB gene.Mitochondrion. 2019 Jul;47:24-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Mitochondrion. 2019. PMID: 30986505 Clinical Trial.
-
Megaconial congenital muscular dystrophy due to novel CHKB variants: a case report and literature review.Skelet Muscle. 2022 Sep 29;12(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13395-022-00306-8. Skelet Muscle. 2022. PMID: 36175989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Megaconial congenital muscular dystrophy due to CHKB gene variants, the first report of thirteen Iranian patients.Neuromuscul Disord. 2023 Jul;33(7):589-595. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2023.06.006. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Neuromuscul Disord. 2023. PMID: 37393748
Cited by
-
Identification of new genetic polymorphisms that alter the dietary requirement for choline and vary in their distribution across ethnic and racial groups.FASEB J. 2014 Jul;28(7):2970-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-249557. Epub 2014 Mar 26. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24671709 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of Skin Changes in the Differential Diagnosis of Congenital Muscular Dystrophies.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3128735. doi: 10.1155/2016/3128735. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27123443 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitochondria-Lysosome Contacts in Neurogenetic Diseases.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jan 31;16:784880. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.784880. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35177962 Free PMC article.
-
Critical roles of mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis in tomato development and environmental response.Plant Physiol. 2022 Aug 29;190(1):576-591. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac255. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35640121 Free PMC article.
-
Lipids and synaptic functions.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018 Nov;41(6):1117-1122. doi: 10.1007/s10545-018-0204-1. Epub 2018 Jun 4. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018. PMID: 29869164 Review.
References
-
- Sher R.B., Aoyama C., Huebsch K.A., Ji S., Kerner J., Yang Y., Frankel W.N., Hoppel C.L., Wood P.A., Vance D.E., Cox G.A. A rostrocaudal muscular dystrophy caused by a defect in choline kinase beta, the first enzyme in phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:4938–4948. - PubMed
-
- Nishino I., Kobayashi O., Goto Y., Kurihara M., Kumagai K., Fujita T., Hashimoto K., Horai S., Nonaka I. A new congenital muscular dystrophy with mitochondrial structural abnormalities. Muscle Nerve. 1998;21:40–47. - PubMed
-
- Liao H., Aoyama C., Ishidate K., Teraoka H. Deletion and alanine mutation analyses for the formation of active homo- or hetero-dimer complexes of mouse choline kinase-α and -β. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1761:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama C., Yamazaki N., Terada H., Ishidate K. Structure and characterization of the genes for murine choline/ethanolamine kinase isozymes alpha and beta. J. Lipid Res. 2000;41:452–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

