Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: innovative trends and prospects
- PMID: 21447010
- PMCID: PMC11158341
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01941.x
Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: innovative trends and prospects
Abstract
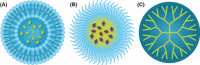
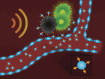
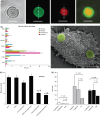
Cancer is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with recent advancements resulting in modest impacts on patient survival. Nanomedicine represents an innovative field with immense potential for improving cancer treatment, having ushered in several established drug delivery platforms. Nanoconstructs such as liposomes are widely used in clinics, while polymer micelles are in advanced phases of clinical trials in several countries. Currently, the field of nanomedicine is generating a new wave of nanoscale drug delivery strategies, embracing trends that involve the functionalization of these constructs with moieties that enhance site-specific delivery and tailored release. Herein, we discuss several advancements in established nanoparticle technologies such as liposomes, polymer micelles, and dendrimers regarding tumor targeting and controlled release strategies, which are being incorporated into their design with the hope of generating a more robust and efficacious nanotherapeutic modality. We also highlight a novel strategy known as multistage drug delivery; a rationally designed nanocarrier aimed at overcoming numerous biological barriers involved in drug delivery through the decoupling of various tasks that comprise the journey from the moment of systemic administration to arrival at the tumor site.
© 2011 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
Ultrasound-Mediated Cancer Therapeutics Delivery using Micelles and Liposomes: A Review.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2021;16(4):498-520. doi: 10.2174/1574892816666210706155110. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34911412 Review.
-
Emerging nanotherapeutic strategies in breast cancer.Breast. 2014 Feb;23(1):10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Breast. 2014. PMID: 24215984 Review.
-
Targeted nanoparticulate drug-delivery systems for treatment of solid tumors: a review.Ther Deliv. 2010 Nov;1(5):713-34. doi: 10.4155/tde.10.47. Ther Deliv. 2010. PMID: 22833959 Review.
-
Nanomedicines based drug delivery systems for anti-cancer targeting and treatment.Curr Drug Deliv. 2015;12(2):177-91. doi: 10.2174/1567201811666140822112516. Curr Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25146439 Review.
Cited by
-
Margination of micro- and nano-particles in blood flow and its effect on drug delivery.Sci Rep. 2014 May 2;4:4871. doi: 10.1038/srep04871. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24786000 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol-loaded nanomedicines for cancer applications.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2021 Jun;4(3):e1353. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1353. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 33655717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Covalent Organic Frameworks as Nanocarriers for Improved Delivery of Chemotherapeutic Agents.Materials (Basel). 2022 Oct 16;15(20):7215. doi: 10.3390/ma15207215. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery to the central nervous system.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 May 15;64(7):701-5. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2011.12.006. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012. PMID: 22210134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanostructures for site-specific delivery of oxaliplatin cancer therapy: Versatile nanoplatforms in synergistic cancer therapy.Transl Oncol. 2024 Jan;39:101838. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101838. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38016356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010; 60: 277–300. - PubMed
-
- Pegram MD, Konecny G, Slamon DJ. The molecular and cellular biology of HER2/neu gene amplification/overexpression and the clinical development of herceptin (trastuzumab) therapy for breast cancer. Cancer Treat Res 2000; 103: 57–75. - PubMed
-
- Peer D, Karp JM, Hong S, Farokhzad OC, Margalit R, Langer R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat Nanotechnol 2007; 2: 751–60. - PubMed
-
- Olson RD, Mushlin PS. Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity: analysis of prevailing hypotheses. FASEB J 1990; 4: 3076–86. - PubMed
-
- Strebhardt K, Ullrich A. Paul Ehrlich’s magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress. Nat Rev 2008; 8: 473–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

