CDKL5, a protein associated with rett syndrome, regulates neuronal morphogenesis via Rac1 signaling
- PMID: 20861382
- PMCID: PMC6633570
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1102-10.2010
CDKL5, a protein associated with rett syndrome, regulates neuronal morphogenesis via Rac1 signaling
Abstract
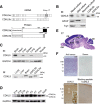
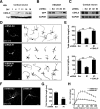
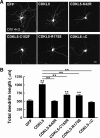
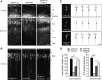
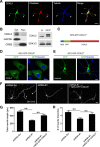
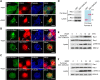
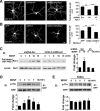
Mutations in cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5), also known as serine/threonine kinase 9 (STK9), have been identified in patients with Rett syndrome (RTT) and X-linked infantile spasm. However, the function of CDKL5 in the brain remains unknown. Here, we report that CDKL5 is a critical regulator of neuronal morphogenesis. We identified a neuron-specific splicing variant of CDKL5 whose expression was markedly induced during postnatal development of the rat brain. Downregulating CDKL5 by RNA interference (RNAi) in cultured cortical neurons inhibited neurite growth and dendritic arborization, whereas overexpressing CDKL5 had opposite effects. Furthermore, knocking down CDKL5 in the rat brain by in utero electroporation resulted in delayed neuronal migration, and severely impaired dendritic arborization. In contrast to its proposed function in the nucleus, we found that CDKL5 regulated dendrite development through a cytoplasmic mechanism. In fibroblasts and in neurons, CDKL5 colocalized and formed a protein complex with Rac1, a critical regulator of actin remodeling and neuronal morphogenesis. Overexpression of Rac1 prevented the inhibition of dendrite growth caused by CDKL5 knockdown, and the growth-promoting effect of ectopically expressed CDKL5 on dendrites was abolished by coexpressing a dominant-negative form of Rac1. Moreover, CDKL5 was required for brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-induced activation of Rac1. Together, these results demonstrate a critical role of CDKL5 in neuronal morphogenesis and identify a Rho GTPase signaling pathway which may contribute to CDKL5-related disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synaptic synthesis, dephosphorylation, and degradation: a novel paradigm for an activity-dependent neuronal control of CDKL5.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 13;290(7):4512-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.589762. Epub 2015 Jan 2. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25555910 Free PMC article.
-
Pak1 is involved in dendrite initiation as a downstream effector of Rac1 in cortical neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002 Aug;20(4):579-94. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2002.1144. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12213441
-
Myo9b and RICS modulate dendritic morphology of cortical neurons.Cereb Cortex. 2013 Jan;23(1):71-9. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhr378. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Cereb Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22250289
-
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase-Like 5 (CDKL5): Possible Cellular Signalling Targets and Involvement in CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder.Neural Plast. 2020 Jun 5;2020:6970190. doi: 10.1155/2020/6970190. eCollection 2020. Neural Plast. 2020. PMID: 32587608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and Synaptic Bases of CDKL5 Disorder.Dev Neurobiol. 2019 Jan;79(1):8-19. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22639. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Dev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30246934 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of CDKL5 disrupts kinome profile and event-related potentials leading to autistic-like phenotypes in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 26;109(52):21516-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216988110. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23236174 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Production of CDKL5 Catalytic Domain: Insights in Aggregation, Internal Translation and Phosphorylation Patterns.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 15;25(16):8891. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168891. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201578 Free PMC article.
-
CDKL5 ensures excitatory synapse stability by reinforcing NGL-1-PSD95 interaction in the postsynaptic compartment and is impaired in patient iPSC-derived neurons.Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Sep;14(9):911-23. doi: 10.1038/ncb2566. Epub 2012 Aug 26. Nat Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22922712 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Visual Impairment in CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder.Front Neurol. 2022 Jan 26;12:805745. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.805745. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35153983 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral Visual Impairment in CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder Correlates With Developmental Achievement.J Child Neurol. 2021 Oct;36(11):974-980. doi: 10.1177/08830738211019284. J Child Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34547934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong D, Dunn JK, Antalffy B, Trivedi R. Selective dendritic alterations in the cortex of Rett syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1995;54:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Bertani I, Rusconi L, Bolognese F, Forlani G, Conca B, De Monte L, Badaracco G, Landsberger N, Kilstrup-Nielsen C. Functional consequences of mutations in CDKL5, an X-linked gene involved in infantile spasms and mental retardation. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:32048–32056. - PubMed
-
- Chang Q, Khare G, Dani V, Nelson S, Jaenisch R. The disease progression mutant mice is affected of Mecp2 by the level of BDNF expression. Neuron. 2006;49:341–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
