Nephronophthisis
- PMID: 20652329
- PMCID: PMC4160028
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-010-1585-z
Nephronophthisis
Abstract
Nephronophthisis (NPHP) is an autosomal recessive cystic kidney disease and the most frequent genetic cause of end-stage renal disease up to the third decade of life. It is caused by mutations in 11 different genes, denoted nephrocystins (NPHP1-11, NPHP1L). As an increasing number of these genes are identified, our knowledge of nephronophthisis is changing, thereby improving our understanding of the pathomechanisms in NPHP. Recent publications have described ciliary expression of nephrocystins together with other cystoproteins, such as polycystins 1 and 2 and fibrocystin. These findings have shifted our focus to a pathomechanism involving defects in ciliary function (ciliopathy) and planar cell polarity (PCP). In addition, discoveries of new nephrocystin genes have shown that the disease spectrum of NPHP is much broader than previously anticipated. Different forms of mutations within the same NPHP gene can cause different disease severity. In this review, we highlight the different hypotheses on the pathomechanisms for NPHP and underline the clinical variability of this disease. The clinical spectrum has become even more complex with the possibility of oligogenicity in NPHP.
Figures
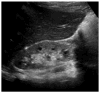
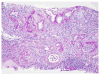
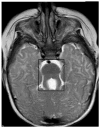

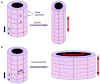
Similar articles
-
Nephronophthisis-associated ciliopathies.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Jun;18(6):1855-71. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006121344. Epub 2007 May 18. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17513324 Review.
-
Nephronophthisis: disease mechanisms of a ciliopathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Jan;20(1):23-35. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008050456. Epub 2008 Dec 31. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19118152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutations in INVS encoding inversin cause nephronophthisis type 2, linking renal cystic disease to the function of primary cilia and left-right axis determination.Nat Genet. 2003 Aug;34(4):413-20. doi: 10.1038/ng1217. Nat Genet. 2003. PMID: 12872123 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of oligogenic inheritance in nephronophthisis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Oct;18(10):2789-95. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007020243. Epub 2007 Sep 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17855640
-
Clinical characterization and NPHP1 mutations in nephronophthisis and associated ciliopathies: a single center experience.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2012 Sep;23(5):1090-8. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.100968. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2012. PMID: 22982934 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of 99 novel mutations in a worldwide cohort of 1,056 patients with a nephronophthisis-related ciliopathy.Hum Genet. 2013 Aug;132(8):865-84. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1297-0. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23559409 Free PMC article.
-
Ciliogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans requires genetic interactions between ciliary middle segment localized NPHP-2 (inversin) and transition zone-associated proteins.J Cell Sci. 2012 Jun 1;125(Pt 11):2592-603. doi: 10.1242/jcs.095539. Epub 2012 Mar 5. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22393243 Free PMC article.
-
The Han:SPRD Rat: A Preclinical Model of Polycystic Kidney Disease.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 3;12(2):362. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020362. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38397964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of renal cyst cells of type I Nephronophthisis by single-nucleus RNA sequencing.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jul 31;11:1192935. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1192935. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37583898 Free PMC article.
-
Ciliopathies: an expanding disease spectrum.Pediatr Nephrol. 2011 Jul;26(7):1039-56. doi: 10.1007/s00467-010-1731-7. Epub 2011 Jan 6. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21210154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith C, Grham J. Congenital medullary cysts of the kidneys with severe refractory anemia. Am J Dis Child. 1945;69:369–377.
-
- Fanconi G, Hanhart E, von Albertini A, Uhlinger E, Dolivo G, Prader A. Familial, juvenile nephronophthisis (idiopathic parenchymal contracted kidney) Helv Paediatr Acta. 1951;6:1–49. - PubMed
-
- Hildebrandt F, Otto E. Cilia and centrosomes: a unifying pathogenic concept for cystic kidney disease? Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:928–940. - PubMed
-
- Hildebrandt F, Strahm B, Nothwang H-G, Gretz N, Schnieders B, Singh-Sawhney I, Kutt R, Vollmer M Brandis Mmembers of the APN study group . Molecular genetic identification of families with juvenile nephronophthisis type 1: rate of progression to renal failure. Kindey Int. 1997;51:261–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
