First-in-human mutation-targeted siRNA phase Ib trial of an inherited skin disorder
- PMID: 19935778
- PMCID: PMC2839285
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2009.273
First-in-human mutation-targeted siRNA phase Ib trial of an inherited skin disorder
Abstract
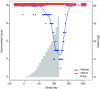
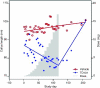
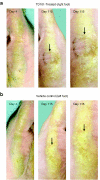
The rare skin disorder pachyonychia congenita (PC) is an autosomal dominant syndrome that includes a disabling plantar keratoderma for which no satisfactory treatment is currently available. We have completed a phase Ib clinical trial for treatment of PC utilizing the first short-interfering RNA (siRNA)-based therapeutic for skin. This siRNA, called TD101, specifically and potently targets the keratin 6a (K6a) N171K mutant mRNA without affecting wild-type K6a mRNA. The safety and efficacy of TD101 was tested in a single-patient 17-week, prospective, double-blind, split-body, vehicle-controlled, dose-escalation trial. Randomly assigned solutions of TD101 or vehicle control were injected in symmetric plantar calluses on opposite feet. No adverse events occurred during the trial or in the 3-month washout period. Subjective patient assessment and physician clinical efficacy measures revealed regression of callus on the siRNA-treated, but not on the vehicle-treated foot. This trial represents the first time that siRNA has been used in a clinical setting to target a mutant gene or a genetic disorder, and the first use of siRNA in human skin. The callus regression seen on the patient's siRNA-treated foot appears sufficiently promising to warrant additional studies of siRNA in this and other dominant-negative skin diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-nucleotide-specific siRNA targeting in a dominant-negative skin model.J Invest Dermatol. 2008 Mar;128(3):594-605. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701060. Epub 2007 Oct 11. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 17914454
-
Development of quantitative molecular clinical end points for siRNA clinical trials.J Invest Dermatol. 2011 May;131(5):1029-36. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.372. Epub 2010 Dec 30. J Invest Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21191405
-
Use of self-delivery siRNAs to inhibit gene expression in an organotypic pachyonychia congenita model.J Invest Dermatol. 2011 May;131(5):1037-44. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.426. Epub 2011 Jan 20. J Invest Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21248764
-
The phenotypic and molecular genetic features of pachyonychia congenita.J Invest Dermatol. 2011 May;131(5):1015-7. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.59. Epub 2011 Mar 24. J Invest Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21430705 Review.
-
Therapy for dominant inherited diseases by allele-specific RNA interference: successes and pitfalls.Curr Gene Ther. 2015;15(5):503-10. doi: 10.2174/1566523215666150812115730. Curr Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 26264709 Review.
Cited by
-
Antisense-induced messenger depletion corrects a COL6A2 dominant mutation in Ullrich myopathy.Hum Gene Ther. 2012 Dec;23(12):1313-8. doi: 10.1089/hum.2012.109. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Hum Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22992134 Free PMC article.
-
Topical delivery of siRNA-based spherical nucleic acid nanoparticle conjugates for gene regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 24;109(30):11975-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118425109. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22773805 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Intravital Imaging of siRNA-Mediated Mutant Keratin Gene Repression in Skin.Mol Imaging Biol. 2016 Feb;18(1):34-42. doi: 10.1007/s11307-015-0875-z. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016. PMID: 26169581
-
Controlling fibrous capsule formation through long-term down-regulation of collagen type I (COL1A1) expression by nanofiber-mediated siRNA gene silencing.Acta Biomater. 2013 Jan;9(1):4513-24. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.09.029. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Acta Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23036951 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of the cutaneous phenotype in inherited disorders of cholesterol metabolism: Therapeutic implications for topical treatment of these disorders.Dermatoendocrinol. 2011 Apr;3(2):100-6. doi: 10.4161/derm.3.2.14831. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Dermatoendocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21695019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Novobrantseva TI, Akinc A, Borodovsky A., and , de Fougerolles A. Delivering silence: advancements in developing siRNA therapeutics. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008;11:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen T, Menocal EM, Harborth J., and , Fruehauf JH. RNAi therapeutics: an update on delivery. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2008;10:158–167. - PubMed
-
- Haussecker D. The business of RNAi therapeutics. Hum Gene Ther. 2008;19:451–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

