Reduced TFAP2A function causes variable optic fissure closure and retinal defects and sensitizes eye development to mutations in other morphogenetic regulators
- PMID: 19685247
- PMCID: PMC3083835
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-009-0730-x
Reduced TFAP2A function causes variable optic fissure closure and retinal defects and sensitizes eye development to mutations in other morphogenetic regulators
Abstract
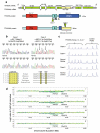
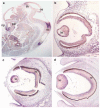
Mutations in the transcription factor encoding TFAP2A gene underlie branchio-oculo-facial syndrome (BOFS), a rare dominant disorder characterized by distinctive craniofacial, ocular, ectodermal and renal anomalies. To elucidate the range of ocular phenotypes caused by mutations in TFAP2A, we took three approaches. First, we screened a cohort of 37 highly selected individuals with severe ocular anomalies plus variable defects associated with BOFS for mutations or deletions in TFAP2A. We identified one individual with a de novo TFAP2A four amino acid deletion, a second individual with two non-synonymous variations in an alternative splice isoform TFAP2A2, and a sibling-pair with a paternally inherited whole gene deletion with variable phenotypic expression. Second, we determined that TFAP2A is expressed in the lens, neural retina, nasal process, and epithelial lining of the oral cavity and palatal shelves of human and mouse embryos--sites consistent with the phenotype observed in patients with BOFS. Third, we used zebrafish to examine how partial abrogation of the fish ortholog of TFAP2A affects the penetrance and expressivity of ocular phenotypes due to mutations in genes encoding bmp4 or tcf7l1a. In both cases, we observed synthetic, enhanced ocular phenotypes including coloboma and anophthalmia when tfap2a is knocked down in embryos with bmp4 or tcf7l1a mutations. These results reveal that mutations in TFAP2A are associated with a wide range of eye phenotypes and that hypomorphic tfap2a mutations can increase the risk of developmental defects arising from mutations at other loci.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel TFAP2A mutation in familial Branchio-Oculo-Facial Syndrome with predominant ocular phenotype.Ophthalmic Genet. 2011 Nov;32(4):250-5. doi: 10.3109/13816810.2011.592176. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Ophthalmic Genet. 2011. PMID: 21728810
-
TFAP2A mutations result in branchio-oculo-facial syndrome.Am J Hum Genet. 2008 May;82(5):1171-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.03.005. Am J Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18423521 Free PMC article.
-
A family with branchio-oculo-facial syndrome with primarily ocular involvement associated with mutation of the TFAP2A gene.Ophthalmic Genet. 2012 Jun;33(2):100-6. doi: 10.3109/13816810.2011.634878. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Ophthalmic Genet. 2012. PMID: 22191992
-
Ocular manifestations of branchio-oculo-facial syndrome: report of a novel mutation and review of the literature.Mol Vis. 2010 May 8;16:813-8. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20461149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Genetic analysis of a Chinese pedigree affected with Branchio-oculo-facial syndrome and a literature review].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Sep 10;41(9):1084-1089. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511374-20230720-00008. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39217487 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Kiwi genome provides insights into evolution of a nocturnal lifestyle.Genome Biol. 2015 Jul 23;16(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0711-4. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 26201466 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a driving force regulating gene expression in bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) larvae development.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 5;14(1):23191. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74152-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39369082 Free PMC article.
-
Potential prognosis and immunotherapy predictor TFAP2A in pan-cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jan 23;16(2):1021-1048. doi: 10.18632/aging.205225. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38265973 Free PMC article.
-
Looking to the future of zebrafish as a model to understand the genetic basis of eye disease.Hum Genet. 2019 Sep;138(8-9):993-1000. doi: 10.1007/s00439-019-02055-z. Epub 2019 Aug 17. Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31422478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel TFAP2A mutation in a Japanese family with Branchio-oculo-facial syndrome.Hum Genome Var. 2018 May 10;5:5. doi: 10.1038/s41439-018-0004-z. eCollection 2018. Hum Genome Var. 2018. PMID: 29760939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler R, Belecky-Adams TL. The role of bone morphogenetic proteins in the differentiation of the ventral optic cup. Development. 2002;129(13):3161–3171. - PubMed
-
- Ahituv N, Erven A, Fuchs H, Guy K, Ashery-Padan R, Williams T, de Angelis MH, Avraham KB, Steel KP. An ENU-induced mutation in AP-2alpha leads to middle ear and ocular defects in Doarad mice. Mamm Genome. 2004;15(6):424–432. - PubMed
-
- Asai-Coakwell M, French CR, Ye M, Garcha K, Bigot K, Perera AG, Staehling-Hampton K, Mema SC, Chanda B, Mushegian A, Bamforth S, et al. Incomplete penetrance and phenotypic variability characterize Gdf6-attributable oculo-skeletal phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18(6):1110–1121. - PubMed
-
- Bakrania P, Efthymiou M, Klein JC, Salt A, Bunyan DJ, Wyatt A, Ponting CP, Martin A, Williams S, Lindley V, Gilmore J, et al. Mutations in BMP4 cause eye, brain, and digit developmental anomalies: overlap between the BMP4 and hedgehog signaling pathways. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82(2):304–319. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barrallo-Gimeno A, Holzschuh J, Driever W, Knapik EW. Neural crest survival and differentiation in zebrafish depends on mont blanc/tfap2a gene function. Development. 2004;131(7):1463–1477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

