Microcephalin and pericentrin regulate mitotic entry via centrosome-associated Chk1
- PMID: 19546241
- PMCID: PMC2712957
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200810159
Microcephalin and pericentrin regulate mitotic entry via centrosome-associated Chk1
Abstract
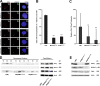
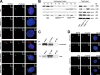
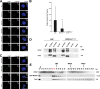
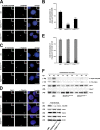
Primary microcephaly, Seckel syndrome, and microcephalic osteodysplastic primordial dwarfism type II (MOPD II) are disorders exhibiting marked microcephaly, with small brain sizes reflecting reduced neuron production during fetal life. Although primary microcephaly can be caused by mutations in microcephalin (MCPH1), cells from patients with Seckel syndrome and MOPD II harbor mutations in ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related (ATR) or pericentrin (PCNT), leading to disturbed ATR signaling. In this study, we show that a lack of MCPH1 or PCNT results in a loss of Chk1 from centrosomes with subsequently deregulated activation of centrosomal cyclin B-Cdk1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of mitotic entry by microcephalin and its overlap with ATR signalling.Nat Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;8(7):725-33. doi: 10.1038/ncb1431. Epub 2006 Jun 18. Nat Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16783362
-
MCPH1 regulates the neuroprogenitor division mode by coupling the centrosomal cycle with mitotic entry through the Chk1-Cdc25 pathway.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Sep 25;13(11):1325-34. doi: 10.1038/ncb2342. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21947081
-
Centrosomal Che-1 protein is involved in the regulation of mitosis and DNA damage response by mediating pericentrin (PCNT)-dependent Chk1 protein localization.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 9;288(32):23348-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.465302. Epub 2013 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23798705 Free PMC article.
-
Microcephalin: a causal link between impaired damage response signalling and microcephaly.Cell Cycle. 2006 Oct;5(20):2339-44. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.20.3358. Epub 2006 Oct 16. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 17102619 Review.
-
Consequences of Centrosome Dysfunction During Brain Development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1002:19-45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-57127-0_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28600781 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations in ORC1, encoding the largest subunit of the origin recognition complex, cause microcephalic primordial dwarfism resembling Meier-Gorlin syndrome.Nat Genet. 2011 Feb 27;43(4):350-5. doi: 10.1038/ng.776. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 21358633
-
A novel homozygous mutation of the PCNT gene in a Chinese patient with microcephalic osteodysplastic primordial dwarfism type II.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021 Sep;9(9):e1761. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1761. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021. PMID: 34331829 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-dependent localization of CHK2 at centrosomes during mitosis.Cell Div. 2013 May 16;8(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-8-7. Cell Div. 2013. PMID: 23680298 Free PMC article.
-
Primary microcephaly: do all roads lead to Rome?Trends Genet. 2009 Nov;25(11):501-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2009.09.011. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Trends Genet. 2009. PMID: 19850369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and pathways of growth failure in primordial dwarfism.Genes Dev. 2011 Oct 1;25(19):2011-24. doi: 10.1101/gad.169037. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21979914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alderton G.K., Joenje H., Varon R., Borglum A.D., Jeggo P.A., O'Driscoll M. 2004. Seckel syndrome exhibits cellular features demonstrating defects in the ATR-signalling pathway.Hum. Mol. Genet. 13:3127–3138 - PubMed
-
- Alderton G.K., Galbiati L., Griffith E., Surinya K.H., Neitzel H., Jackson A.P., Jeggo P.A., O'Driscoll M. 2006. Regulation of mitotic entry by microcephalin and its overlap with ATR signalling.Nat. Cell Biol. 8:725–733 - PubMed
-
- Bailly E., Pines J., Hunter T., Bornens M. 1992. Cytoplasmic accumulation of cyclin B1 in human cells: association with a detergent-resistant compartment within the centrosome.J. Cell Sci. 101:529–545 - PubMed
-
- Bond J., Woods C.G. 2006. Cytoskeletal genes regulating brain size.Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18:95–101 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

