Zinc finger protein Zbtb20 is essential for postnatal survival and glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 19273596
- PMCID: PMC2682054
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01667-08
Zinc finger protein Zbtb20 is essential for postnatal survival and glucose homeostasis
Abstract
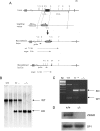
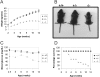
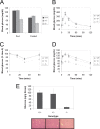
Zbtb20 is a member of the POK family of proteins, which function primarily as transcriptional repressors via interactions mediated by their conserved C(2)H(2) Krüppel type zinc finger and BTB/POZ domains. To define the function of Zbtb20 in vivo, we generated knockout mice by homologous recombination. Zbtb20 null mice display a stark phenotype characterized by postnatal growth retardation, metabolic dysfunction, and lethality. Zbtb20 knockout mice displayed abnormal glucose homeostasis, hormonal responses, and depletion of energy stores, consistent with an energetic deficit. Additionally, increased serum bilirubin and alanine aminotransferase levels were suggestive of liver dysfunction. To identify potential liver-specific Zbtb20 target genes, we performed transcript profiling studies on liver tissue from Zbtb20 knockout mice and wild-type littermate controls. These studies identified sets of genes involved in growth, metabolism, and detoxification that were differentially regulated in Zbtb20 knockout liver. Transgenic mice expressing Zbtb20 in the liver were generated and crossed onto the Zbtb20 knockout background, which resulted in no significant normalization of growth or glucose metabolism but a significant increase in life span compared to controls. These data indicate that the phenotype of Zbtb20 knockout mice results from liver-dependent and -independent defects, suggesting that Zbtb20 plays nonredundant roles in multiple organ systems.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zinc finger protein ZBTB20 is an independent prognostic marker and promotes tumor growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing FoxO1.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):14336-49. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7425. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26893361 Free PMC article.
-
The zinc finger protein ZBTB20 regulates transcription of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 and β cell function in mice.Gastroenterology. 2012 Jun;142(7):1571-1580.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.02.043. Epub 2012 Feb 25. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22374165
-
Regulation of hepatic lipogenesis by the zinc finger protein Zbtb20.Nat Commun. 2017 Mar 22;8:14824. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14824. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28327662 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Finger and BTB Domain-Containing 20: A Newly Emerging Player in Pathogenesis and Development of Human Cancers.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 4;14(2):192. doi: 10.3390/biom14020192. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription Factor Zbtb20 as a Regulator of Malignancy and Its Practical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 6;24(18):13763. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813763. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Berberine ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by a global modulation of hepatic mRNA and lncRNA expression profiles.J Transl Med. 2015 Jan 27;13:24. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0383-6. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25623289 Free PMC article.
-
An Infant With Primrose Syndrome: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Oct 5;15(10):e46546. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46546. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37927765 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in ZBTB20 cause Primrose syndrome.Nat Genet. 2014 Aug;46(8):815-7. doi: 10.1038/ng.3035. Epub 2014 Jul 13. Nat Genet. 2014. PMID: 25017102
-
Zbtb20 is essential for the specification of CA1 field identity in the developing hippocampus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 6;107(14):6510-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912315107. Epub 2010 Mar 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20308569 Free PMC article.
-
ZBTB20 is essential for cochlear maturation and hearing in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 13;120(24):e2220867120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2220867120. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37279265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butler, A. A., and D. Le Roith. 2001. Control of growth by the somatropic axis: growth hormone and the insulin-like growth factors have related and independent roles. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 63141-164. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, S. E., E. Kokkotou, S. B. Biddinger, T. Kondo, R. Gebhardt, J. Kratzsch, C. S. Mantzoros, and C. R. Kahn. 2007. High circulating leptin receptors with normal leptin sensitivity in liver-specific insulin receptor knock-out (LIRKO) mice. J. Biol. Chem. 28223672-23678. - PubMed
-
- Costoya, J. A. 2007. Functional analysis of the role of POK transcriptional repressors. Brief. Funct. Genomics Proteomics 68-18. - PubMed
-
- Dentin, R., J. P. Pegorier, F. Benhamed, F. Foufelle, P. Ferre, V. Fauveau, M. A. Magnuson, J. Girard, and C. Postic. 2004. Hepatic glucokinase is required for the synergistic action of ChREBP and SREBP-1c on glycolytic and lipogenic gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 27920314-20326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
