Carriers of recessive WNK1/HSN2 mutations for hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 2 (HSAN2) are more sensitive to thermal stimuli
- PMID: 19228968
- PMCID: PMC2749662
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4633-08.2009
Carriers of recessive WNK1/HSN2 mutations for hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 2 (HSAN2) are more sensitive to thermal stimuli
Abstract
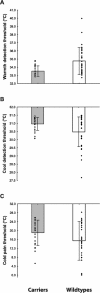
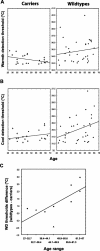
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 2 (HSAN2) is a rare recessive genetic disorder characterized by severe sensory loss affecting the tactile, thermal and nociceptive modalities. Although heterozygous carriers of nonsense mutations in the HSN2 gene, called with-no-lysine(K)-1 (WNK1), do not develop the disease, historical and experimental evidence suggests that these individuals might perceive somatosensory stimuli differently from others. Using the method-of-limits, we assessed the thresholds for warmth detection, cool detection, heat pain and cold pain in 25 mutation carriers and 35 controls. In group analyses, carriers displayed significantly lower warmth (p<0.001) and cool (p<0.05) difference thresholds, and also tended to report cold pain at higher temperatures (p=0.095), than controls. Similarly, matched-pair analyses showed that carriers are significantly more sensitive to warm stimuli (p<0.01) and cold pain stimuli (p<0.05), and tend to be more sensitive to cool stimuli (p=0.11). Furthermore, the differences between the warmth detection thresholds of the carriers and those of gender- and sex-matched wild types significantly increased with age (r=0.76, p=0.02), and in carriers cool detection thresholds did not increase with age (r=0.27, p=0.24) as expected and observed in controls (r=0.34, p=0.05). This study demonstrates that the carriers of a recessive mutation for HSAN2 display greater sensitivity to innocuous thermal stimuli, as well as for cold pain, suggesting a possible environmental adaptive advantage of the heterozygous state.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two mutations in the HSN2 gene explain the high prevalence of HSAN2 in French Canadians.Neurology. 2005 May 24;64(10):1762-7. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000161849.29944.43. Neurology. 2005. PMID: 15911806
-
Expression pattern analysis and characterization of the hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy 2 A (HSAN2A) gene with no lysine kinase (WNK1) in human dorsal root ganglion.Exp Neurol. 2023 Dec;370:114552. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114552. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Exp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37793538
-
Arthropathy-related pain in a patient with congenital impairment of pain sensation due to hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type II with a rare mutation in the WNK1/HSN2 gene: a case report.BMC Neurol. 2016 Oct 21;16(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0727-8. BMC Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27765018 Free PMC article.
-
Oral manifestations, dental management, and a rare homozygous mutation of the PRDM12 gene in a boy with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type VIII: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2017 Aug 15;11(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s13256-017-1387-z. J Med Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28807049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular genetics of hereditary sensory neuropathies.Neuromolecular Med. 2006;8(1-2):147-58. doi: 10.1385/nmm:8:1-2:147. Neuromolecular Med. 2006. PMID: 16775373 Review.
Cited by
-
SPAK/OSR1 regulate NKCC1 and WNK activity: analysis of WNK isoform interactions and activation by T-loop trans-autophosphorylation.Biochem J. 2012 Jan 1;441(1):325-37. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111879. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22032326 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic pain loss disorders.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022 Jun 16;8(1):41. doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00365-7. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022. PMID: 35710757 Review.
-
The WNKs: atypical protein kinases with pleiotropic actions.Physiol Rev. 2011 Jan;91(1):177-219. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00017.2010. Physiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21248166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of WNK1 in pathologic central nervous system signaling.Ann Neurosci. 2011 Apr;18(2):70-5. doi: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.1118212. Ann Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 25205925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broadening the Spectrum of Adulthood X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy: A Report of Two Atypical Cases.Front Neurol. 2019 Feb 6;10:70. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00070. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30787906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auer-Grumbach M, Mauko B, Auer-Grumbach P, Pieber TR. Molecular genetics of hereditary sensory neuropathies. Neuromolecular Med. 2006;8:147–158. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod FB, Hilz MJ. Inherited autonomic neuropathies. Semin Neurol. 2003;23:381–390. - PubMed
-
- Cho HJ, Kim BJ, Suh YL, An JY, Ki CS. Novel mutation in the HSN2 gene in a Korean patient with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 2. J Hum Genet. 2006;51:905–908. - PubMed
-
- Coen K, Pareyson D, Auer-Grumbach M, Buyse G, Goemans N, Claeys KG, Verpoorten N, Laur M, Scaioli V, Salmhofer W, Pieber TR, Nelis E, De Jonghe P, Timmerman V. Novel mutations in the HSN2 gene causing hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type II. Neurology. 2006;66:748–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
