Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases
- PMID: 18003914
- PMCID: PMC2141795
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0707292104
Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases
Abstract
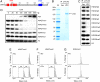
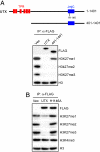
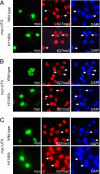
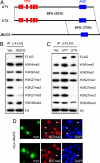
Covalent modifications of histones, such as acetylation and methylation, play important roles in the regulation of gene expression. Histone lysine methylation has been implicated in both gene activation and repression, depending on the specific lysine (K) residue that becomes methylated and the state of methylation (mono-, di-, or trimethylation). Methylation on K4, K9, and K36 of histone H3 has been shown to be reversible and can be removed by site-specific demethylases. However, the enzymes that antagonize methylation on K27 of histone H3 (H3K27), an epigenetic mark important for embryonic stem cell maintenance, Polycomb-mediated gene silencing, and X chromosome inactivation have been elusive. Here we show the JmjC domain-containing protein UTX (ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat, X chromosome), as well as the related JMJD3 (jumonji domain containing 3), specifically removes methyl marks on H3K27 in vitro. Further, the demethylase activity of UTX requires a catalytically active JmjC domain. Finally, overexpression of UTX and JMJD3 leads to reduced di- and trimethylation on H3K27 in cells, suggesting that UTX and JMJD3 may function as H3K27 demethylases in vivo. The identification of UTX and JMJD3 as H3K27-specific demethylases provides direct evidence to indicate that similar to methylation on K4, K9, and K36 of histone H3, methylation on H3K27 is also reversible and can be dynamically regulated by site-specific histone methyltransferases and demethylases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A histone H3 lysine 27 demethylase regulates animal posterior development.Nature. 2007 Oct 11;449(7163):689-94. doi: 10.1038/nature06192. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17851529
-
UTX and JMJD3 are histone H3K27 demethylases involved in HOX gene regulation and development.Nature. 2007 Oct 11;449(7163):731-4. doi: 10.1038/nature06145. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17713478
-
JMJD3 as an epigenetic regulator in development and disease.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;67:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26193001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2, JMJD3, and UTX epigenetically regulate hepatic plasticity inducing retro-differentiation and proliferation of liver cells.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jul 8;10(7):518. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1755-2. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31285428 Free PMC article.
-
H3K27 demethylases, at long last.Cell. 2007 Oct 5;131(1):29-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.026. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17923085 Review.
Cited by
-
Forecasting histone methylation by Polycomb complexes with minute-scale precision.Sci Adv. 2023 Dec 22;9(51):eadj8198. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj8198. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38134278 Free PMC article.
-
Neural growth hormone implicated in body weight sex differences.Endocrinology. 2013 Oct;154(10):3826-35. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1234. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23861378 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral function of Inhibitors-of-kappaB regulates Caenorhabditis elegans development.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 30;10(1):16153. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73146-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32999373 Free PMC article.
-
Utx is required for proper induction of ectoderm and mesoderm during differentiation of embryonic stem cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060020. Epub 2013 Apr 3. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23573229 Free PMC article.
-
UTX, a histone H3-lysine 27 demethylase, acts as a critical switch to activate the cardiac developmental program.Dev Cell. 2012 Jan 17;22(1):25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.11.009. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Dev Cell. 2012. PMID: 22192413 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

