Malformation of cortical and vascular development in one family with parietal foramina determined by an ALX4 homeobox gene mutation
- PMID: 15569759
- PMCID: PMC8148717
Malformation of cortical and vascular development in one family with parietal foramina determined by an ALX4 homeobox gene mutation
Abstract
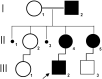
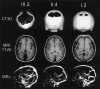
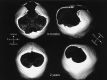
Vascular and cortical anomalies have been found in a family with parietal foramina type 2 (PFM2), which is determined by the ALX4 gene. It is believed that ALX4 has a bone-restricted expression. We report a case of PFM with age-related size variation in a 4-year-old boy, as well as in his mother, aunt and grandfather. MR imaging of the child demonstrates prominent malformations of cortical (polymicrogyric cortex with an unusual infolding pattern) and vascular development (persistence median prosencephalic vein), associated with high tentorial incisure periatrial white matter changes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vertical transmission of a large calvarial ossification defect due to heterozygous variants of ALX4 and TWIST1.Am J Med Genet A. 2021 Mar;185(3):916-922. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62036. Epub 2020 Dec 27. Am J Med Genet A. 2021. PMID: 33369125
-
[Mother and son with enlarged parietal foramina, persistent fetal vein, and ALX4 mutation].No To Hattatsu. 2016 May;48(3):205-8. No To Hattatsu. 2016. PMID: 27349084 Japanese.
-
Enlarged parietal foramina caused by mutations in the homeobox genes ALX4 and MSX2: from genotype to phenotype.Eur J Hum Genet. 2006 Feb;14(2):151-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201526. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16319823 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral Foramina Parietalia Permagna - A Calvarial Defect Caused by Haploinsufficiency of the Msh Homeobox 2 Gene: A Case Report and Current Literature Review.Neuropediatrics. 2024 Jun;55(3):205-208. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1781465. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Neuropediatrics. 2024. PMID: 38447947 Review.
-
Foramina parietalia permagna: familial and radiological evaluation of two cases and review of literature.Childs Nerv Syst. 2017 May;33(5):853-857. doi: 10.1007/s00381-016-3315-8. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Childs Nerv Syst. 2017. PMID: 27975139 Review.
Cited by
-
A Rare Congenital Cause of Epilepsy.Cureus. 2020 Oct 27;12(10):e11204. doi: 10.7759/cureus.11204. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33269135 Free PMC article.
-
ALX4, an epigenetically down regulated tumor suppressor, inhibits breast cancer progression by interfering Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Nov 28;36(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0643-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29183346 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors of the Alx Family: Evolutionarily Conserved Regulators of Deuterostome Skeletogenesis.Front Genet. 2020 Nov 23;11:569314. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.569314. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33329706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracranial and subcutaneous lipoma associated with sagittal sinus fenestration and falcine sinus.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 Jun-Jul;28(6):1034-5. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A0513. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17569951 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial lipoma with extra cranial subcutaneous component with a midline bony defect and persistent falcine sinus.BJR Case Rep. 2023 Jul 22;9(6):20220011. doi: 10.1259/bjrcr.20220011. eCollection 2023 Nov. BJR Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37928707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Little BB, Knoll KA, et al. Hereditary cranium bifidum and symmetric parietal foramina are the same entity. Am J Med Genet 1990;35:453–458 - PubMed
-
- Chrzanowska K, Kozlowski K, Kowalska A. Syndromic foramina parietalia permagna. Am J Med Genet 1998;78:401–405 - PubMed
-
- Wilkie AO, Tang Z, Elanko N, et al. Functional haploinsufficiency of the human homeobox gene MSX2 causes defects in skull ossification. Nat Genet 2000;24:387–390 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
