Disease-causing mutant WNK4 increases paracellular chloride permeability and phosphorylates claudins
- PMID: 15070779
- PMCID: PMC384808
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0306924101
Disease-causing mutant WNK4 increases paracellular chloride permeability and phosphorylates claudins
Abstract
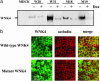
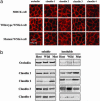
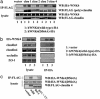
Mutations in the WNK4 gene cause pseudohypoaldosteronism type II (PHAII), an autosomal-dominant disorder of hyperkalemia and hypertension. The target molecules of this putative kinase and the molecular mechanisms by which the mutations cause the phenotypes are currently unknown. Although recent reports found that expression of WNK4 in Xenopus oocytes causes inhibition of the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter and the renal K channel ROMK, there may be additional targets of WNK4. For example, an increase in paracellular chloride permeability has been postulated to be a mediator of PHAII pathogenesis, a possibility supported by the localization of WNK4 at tight junctions in vivo. To determine the validity of this hypothesis, we measured transepithelial Na and Cl permeability in Madin-Darby canine kidney II cells stably expressing wild-type or a pathogenic mutant of WNK4. We found that transepithelial paracellular Cl permeability was increased in cells expressing a disease-causing mutant WNK4 (D564A) but that Na permeability was decreased slightly. Furthermore, WNK4 bound and phosphorylated claudins 1-4, major tight-junction membrane proteins known to be involved in the regulation of paracellular ion permeability. The increases in phosphorylation of claudins were greater in cells expressing the mutant WNK4 than in cells expressing wild-type protein. These results clearly indicate that the pathogenic WNK4 mutant possesses a gain-of-function activity and that the claudins may be important molecular targets of WNK4 kinase. The increased paracellular "chloride shunt" caused by the mutant WNK4 could be the pathogenic mechanism of PHAII.
Figures
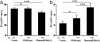

Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Effect of claudins 6 and 9 on paracellular permeability in MDCK II cells.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008 Nov;295(5):R1713-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.90596.2008. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18784328 Free PMC article.
-
Claudins 6, 9, and 13 are developmentally expressed renal tight junction proteins.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):F1132-41. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00063.2006. Epub 2006 Jun 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16774906 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the Ca2+ sensing receptor and the PKC/WNK4 downstream signaling cascade induces incorporation of ZO-2 to tight junctions and its separation from 14-3-3.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Aug 15;30(18):2377-2398. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-09-0591. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31318316 Free PMC article.
-
WNK3 positively regulates epithelial calcium channels TRPV5 and TRPV6 via a kinase-dependent pathway.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008 Nov;295(5):F1472-84. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90229.2008. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18768590 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the kidney anion exchanger 1 affects WNK4 and SPAK phosphorylation and results in claudin-4 phosphorylation.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 13;9(11):e22280. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22280. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38034706 Free PMC article.
-
The kidney-specific WNK1 isoform is induced by aldosterone and stimulates epithelial sodium channel-mediated Na+ transport.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 14;101(50):17434-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408146101. Epub 2004 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15583131 Free PMC article.
-
Tight Junction Proteins and Signaling Pathways in Cancer and Inflammation: A Functional Crosstalk.Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 23;9:1942. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01942. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30728783 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilson, F. H., Disse-Nicodeme, S., Choate, K. A., Ishikawa, K., Nelson-Williams, C., Desitter, I., Gunel, M., Milford, D. V., Lipkin, G. W., Achard, J. M., et al. (2001) Science 293, 1107-1112. - PubMed
-
- Schambelan, M., Sebastian, A. & Rector, F. C., Jr. (1981) Kidney Int. 19, 716-727. - PubMed
-
- Farfel, Z., Iaina, A., Rosenthal, T., Waks, U., Shibolet, S. & Gafni, J. (1978) Arch. Intern. Med. (Moscow) 138, 1828-1832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

