WNK4 regulates apical and basolateral Cl- flux in extrarenal epithelia
- PMID: 14769928
- PMCID: PMC357052
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0308434100
WNK4 regulates apical and basolateral Cl- flux in extrarenal epithelia
Abstract
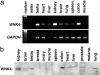
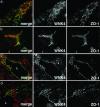
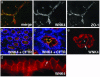
Mutations in the serine-threonine kinase WNK4 [with no lysine (K) 4] cause pseudohypoaldosteronism type II, a Mendelian disease featuring hypertension with hyperkalemia. In the kidney, WNK4 regulates the balance between NaCl reabsorption and K(+) secretion via variable inhibition of the thiazide-sensistive NaCl cotransporter and the K(+) channel ROMK. We now demonstrate expression of WNK4 mRNA and protein outside the kidney. In extrarenal tissues, WNK4 is found almost exclusively in polarized epithelia, variably associating with tight junctions, lateral membranes, and cytoplasm. Epithelia expressing WNK4 include sweat ducts, colonic crypts, pancreatic ducts, bile ducts, and epididymis. WNK4 is also expressed in the specialized endothelium of the blood-brain barrier. These epithelia and endothelium all play important roles in Cl(-) transport. Because WNK4 is known to regulate renal Cl(-) handling, we tested WNK4's effect on the activity of mediators of epithelial Cl(-) flux whose extrarenal expression overlaps with WNK4. WNK4 proved to be a potent inhibitor of the activity of both the Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(-) cotransporter (NKCC1) and the Cl(-)/base exchanger SLC26A6 (CFEX) (>95% inhibition of NKCC1-mediated (86)Rb influx, P < 0.001; >80% inhibition of CFEX-mediated [(14)C] formate uptake, P < 0.001), mediators of Cl(-) flux across basolateral and apical membranes, respectively. In contrast, WNK4 showed no inhibition of pendrin, a related Cl(-)/base exchanger. These findings indicate a general role for WNK4 in the regulation of electrolyte flux in diverse epithelia. Moreover, they reveal that WNK4 regulates the activities of a diverse group of structurally unrelated ion channels, cotransporters, and exchangers.
Figures

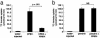
Similar articles
-
WNK1, a kinase mutated in inherited hypertension with hyperkalemia, localizes to diverse Cl- -transporting epithelia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jan 21;100(2):663-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242728499. Epub 2003 Jan 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12522152 Free PMC article.
-
WNK3, a kinase related to genes mutated in hereditary hypertension with hyperkalaemia, regulates the K+ channel ROMK1 (Kir1.1).J Physiol. 2006 Mar 1;571(Pt 2):275-86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.102202. Epub 2005 Dec 15. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16357011 Free PMC article.
-
WNK4 regulates activity of the epithelial Na+ channel in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Mar 6;104(10):4020-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611727104. Epub 2007 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360470 Free PMC article.
-
Role of WNK kinases in regulating tubular salt and potassium transport and in the development of hypertension.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Feb;288(2):F245-52. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00311.2004. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15637347 Review.
-
[WNK1 and WNK4, new players in salt and water homeostasis].Med Sci (Paris). 2005 Jan;21(1):55-60. doi: 10.1051/medsci/200521155. Med Sci (Paris). 2005. PMID: 15639021 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Mechanism and synergism in epithelial fluid and electrolyte secretion.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Aug;466(8):1487-99. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1390-1. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24240699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of potassium (K) handling in the renal collecting duct.Pflugers Arch. 2009 May;458(1):157-68. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0593-3. Epub 2008 Oct 7. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 18839206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of WNK1 in POMC-expressing neurons reduces weigh gain via WNK4-mediated degradation of Kir6.2.Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Oct;447(1-2):165-174. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3301-4. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29392534
-
Paracellular Cl- permeability is regulated by WNK4 kinase: insight into normal physiology and hypertension.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Oct 12;101(41):14877-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406172101. Epub 2004 Oct 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15465913 Free PMC article.
-
SLC26A9 is a Cl(-) channel regulated by the WNK kinases.J Physiol. 2007 Oct 1;584(Pt 1):333-45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.135855. Epub 2007 Aug 2. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17673510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsukita, S., Furuse, M. & Itoh, M. (2001) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 4, 285–293. - PubMed
-
- Wilson, F., Disse-Nicodeme, S., Choate, K., Ishikawa, K., Nelson-Williams, C., Desitter, I., Gunel, M., Milford, D., Lipkin, G., Achard, J., et al. (2001) Science 293, 1107–1112. - PubMed
-
- Kahle, K., Wilson, F., Leng, Q., Lalioti, M., O'Connell, A., Dong, K., Rapson, A., MacGregor, G., Giebisch, G., Hebert, S. & Lifton, R. (2003) Nat. Genet. 4, 372–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

