Mutations in the gene encoding capillary morphogenesis protein 2 cause juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile systemic hyalinosis
- PMID: 14508707
- PMCID: PMC1180602
- DOI: 10.1086/378418
Mutations in the gene encoding capillary morphogenesis protein 2 cause juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile systemic hyalinosis
Abstract
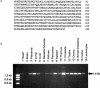
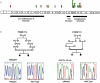
Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis (JHF) and infantile systemic hyalinosis (ISH) are autosomal recessive conditions characterized by multiple subcutaneous skin nodules, gingival hypertrophy, joint contractures, and hyaline deposition. We previously mapped the gene for JHF to chromosome 4q21. We now report the identification of 15 different mutations in the gene encoding capillary morphogenesis protein 2 (CMG2) in 17 families with JHF or ISH. CMG2 is a transmembrane protein that is induced during capillary morphogenesis and that binds laminin and collagen IV via a von Willebrand factor type A (vWA) domain. Of interest, CMG2 also functions as a cellular receptor for anthrax toxin. Preliminary genotype-phenotype analyses suggest that abrogation of binding by the vWA domain results in severe disease typical of ISH, whereas in-frame mutations affecting a novel, highly conserved cytoplasmic domain result in a milder phenotype. These data (1) demonstrate that JHF and ISH are allelic conditions and (2) implicate perturbation of basement-membrane matrix assembly as the cause of the characteristic perivascular hyaline deposition seen in these conditions.
Figures

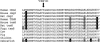
Similar articles
-
Mutations in capillary morphogenesis gene-2 result in the allelic disorders juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile systemic hyalinosis.Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Oct;73(4):957-66. doi: 10.1086/378781. Epub 2003 Sep 12. Am J Hum Genet. 2003. PMID: 12973667 Free PMC article.
-
Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile systemic hyalinosis overlap associated with a novel mutation in capillary morphogenesis protein-2 gene.Am J Dermatopathol. 2007 Feb;29(1):99-103. doi: 10.1097/01.dad.0000245636.39098.e5. Am J Dermatopathol. 2007. PMID: 17284973
-
Spectrum of mutations in the ANTXR2 (CMG2) gene in infantile systemic hyalinosis and juvenile hyaline fibromatosis.Br J Dermatol. 2010 Jul;163(1):213-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09769.x. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Br J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20331448 No abstract available.
-
Systemic Hyalinosis With Heterozygous CMG2 Mutations: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Am J Dermatopathol. 2016 May;38(5):e60-3. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000467. Am J Dermatopathol. 2016. PMID: 26885603 Review.
-
[Infantile systemic hyalinosis: a case report and literature review].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 2;54(12):946-949. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2016.12.015. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27938598 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Infantile Systemic Hyalinosis: Novel Founder Mutation in the Initiation Codon among "Malis (Farmers)" in Jodhpur.Indian J Pediatr. 2016 Nov;83(11):1341-1345. doi: 10.1007/s12098-016-2218-8. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Indian J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27753005
-
Binding of filamentous actin to anthrax toxin receptor 1 decreases its association with protective antigen.Biochemistry. 2012 Feb 14;51(6):1249-56. doi: 10.1021/bi2016469. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22303962 Free PMC article.
-
Converging physiological roles of the anthrax toxin receptors.F1000Res. 2019 Aug 12;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1415. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.19423.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 31448094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MyD88-dependent signaling protects against anthrax lethal toxin-induced impairment of intestinal barrier function.Infect Immun. 2011 Jan;79(1):118-24. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00963-10. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 20974827 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaline fibromatosis syndrome: a case presenting with gingival enlargement as the only clinical manifestation and a report of two new mutations in the ANTXR2 gene.BMC Oral Health. 2021 Oct 9;21(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01840-5. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 34627224 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- BLAST, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/ (for BLAST and tblastn, used in identification of CMG2 paralogs and orthologs)
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for identification of microsatellite markers)
-
- ClustalW, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/ (for alignment of human and orthologous CMG2 and TEM8 proteins)
-
- Conserved Domain Database, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cdd.shtml (for analysis of cytoplasmic domain)
-
- Ensembl, http://www.ensembl.org/ (for mouse cmg2 [Ensembl mouse peptide ENSMUSP00000046348] and fugu tem8 [Ensembl gene SINFRUG00000151577])
References
-
- Allen PW (2001) Selected cases from the Arkadi M. Rywlin International Slide Seminar: hyaline fibromatosis. Adv Anat Pathol 8:173–178 - PubMed
-
- Balci S, Kulacoglu S, Senoz O, Vargel I, Erk Y, Onder S, Gokoz A, Akarsu AN (2002) Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis in three sibs from a consanguineous family: clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical findings. Eur J Hum Genet 10:121
-
- Bell SE, Mavilla A, Salazar R, Bayless KJ, Kanagala S, Maxwell SA, Davis GE (2001) Differential gene expression during capillary morphogenesis in 3D collagen matrices: regulated expression of genes involved in basement membrane matrix assembly, cell cycle progression, cellular differentiation and G-protein signalling. J Cell Sci 114:2755–2773 - PubMed
-
- Bradley KA, Mogridge J, Mourez M, Collier RJ, Young JAT (2001) Identification of the cellular receptor for anthrax toxin. Nature 414:225–229 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

