Structure of factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor 1: An asparaginyl hydroxylase involved in the hypoxic response pathway
- PMID: 12432100
- PMCID: PMC137720
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.202614999
Structure of factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor 1: An asparaginyl hydroxylase involved in the hypoxic response pathway
Abstract
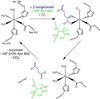
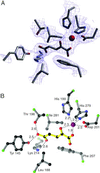
Precise regulation of the evolutionarily conserved hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (HIF) ensures proper adaptation to variations in oxygen availability throughout development and into adulthood. Oxygen-dependent regulation of HIF stability and activity are mediated by hydroxylation of conserved proline and asparagine residues, respectively. Because the relevant prolyl and asparginyl hydroxylases use O(2) to effect these posttranslational modifications, these enzymes are implicated as direct oxygen sensors in the mammalian hypoxic response pathway. Here we present the structure of factor-inhibiting HIF-1 (FIH-1), the pertinent asparaginyl hydroxylase involved in hypoxic signaling. Hydroxylation of the C-terminal transactivation domain (CTAD) of HIF by FIH-1 prevents CTAD association with transcriptional coactivators under normoxic conditions. Consistent with other structurally known hydroxylases, FIH-1 is comprised of a beta-strand jellyroll core with both Fe(II) and the cosubstrate 2-oxoglutarate bound in the active site. Details of the molecular contacts at the active site of FIH-1 have been elucidated and provide a platform for future drug design. Furthermore, the structure reveals the presence of a FIH-1 homodimer that forms in solution and is essential for FIH activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Catalytic properties of the asparaginyl hydroxylase (FIH) in the oxygen sensing pathway are distinct from those of its prolyl 4-hydroxylases.J Biol Chem. 2004 Mar 12;279(11):9899-904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312254200. Epub 2003 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14701857
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) asparagine hydroxylase is identical to factor inhibiting HIF (FIH) and is related to the cupin structural family.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 19;277(29):26351-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200273200. Epub 2002 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12042299
-
Structure of human FIH-1 reveals a unique active site pocket and interaction sites for HIF-1 and von Hippel-Lindau.J Biol Chem. 2003 Feb 28;278(9):7558-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210385200. Epub 2002 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12482756
-
Inhibition of the Oxygen-Sensing Asparaginyl Hydroxylase Factor Inhibiting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor: A Potential Hypoxia Response Modulating Strategy.J Med Chem. 2021 Jun 10;64(11):7189-7209. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00415. Epub 2021 May 24. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34029087 Review.
-
Factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (FIH) and other asparaginyl hydroxylases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Dec;32(Pt 6):943-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0320943. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15506931 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia and hyperbaric oxygen therapy: a review.Int J Gen Med. 2018 Nov 20;11:431-442. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S172460. eCollection 2018. Int J Gen Med. 2018. PMID: 30538529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of inducible chromatin and transcriptional memory in cellular defense system responses to redox-active pollutants.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Jul;170:85-108. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.018. Epub 2021 Mar 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33789123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The facial triad in the α-ketoglutarate dependent oxygenase FIH: A role for sterics in linking substrate binding to O2 activation.J Inorg Biochem. 2017 Jan;166:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Inorg Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27815979 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C-mediated modulation of FIH-1 expression by the homeodomain protein CDP/Cut/Cux.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;27(20):7345-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02201-06. Epub 2007 Aug 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17682059 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear entry and export of FIH are mediated by HIF1α and exportin1, respectively.J Cell Sci. 2018 Nov 19;131(22):jcs219782. doi: 10.1242/jcs.219782. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 30333145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semenza G. L. (2000) Genes Dev. 14 1983-1991. - PubMed
-
- Epstein A. C., Gleadle, J. M., McNeill, L. A., Hewitson, K. S., O'Rourke, J., Mole, D. R., Mukherji, M., Metzen, E., Wilson, M. I., Dhanda, A., et al. (2001) Cell 107 43-54. - PubMed
-
- Bruick R. K. & McKnight, S. L. (2001) Science 294 1337-1340. - PubMed
-
- Jaakkola P., Mole, D. R., Tian, Y.-M., Wilson, M. I., Gielbert, J., Gaskell, S. J., von Kriegsheim, A., Hebestreit, H. F., Mukherji, M., Schofield, C. J., et al. (2001) Science 292 468-472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

