Specific immunoglobulin E responses in ZAP-70-deficient patients are mediated by Syk-dependent T-cell receptor signalling
- PMID: 11412303
- PMCID: PMC1783225
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01246.x
Specific immunoglobulin E responses in ZAP-70-deficient patients are mediated by Syk-dependent T-cell receptor signalling
Abstract
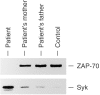
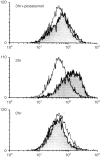
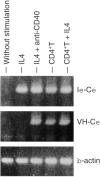
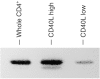
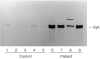
ZAP-70 deficiency is a rare primary immunodeficiency characterized by the absence of peripheral CD8+ T cells and defects in T-cell receptor (TCR) signalling. T cells in ZAP-70-deficient patients are assumed to have no helper functions for B-cell immunoglobulin synthesis, whereas the patients rarely have antigen-specific antibodies. We experienced a ZAP-70-deficient patient, who had immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to food allergens, and we investigated the mechanisms of switching to IgE in the patient. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from the patient did not proliferate upon stimulation with the antigens but produced distinct levels of interleukin-4 (IL-4). Cell sorting analysis indicated that the cells that produced IL-4 in response to the antigens were enriched in CD4+ T cells. Purified CD4+ T cells from the patient produced IL-4 and expressed CD40L upon stimulation with anti-CD3. Moreover, CD4+ T cells pretreated with anti-CD3 induced mature epsilon transcript on naive B cells. Since the results indicated that there remained sufficient T-cell receptor (TCR)-signalling in the patient's T cells to exert antigen-specific IgE switching on B cells, we next investigated the expression of the ZAP-70-homologous kinase Syk. Syk was present in high levels in patient's CD4+ T cells and was tyrosine-phosphorylated after TCR stimulation. Inhibition of Syk by piceatannol resulted in decreased production of IL-4 and expression of CD40L on patient's CD4+ T cells. Moreover, Syk was expressed on all human T-cell leukaemia virus (HTLV-1)-transformed T-cell lines derived from peripheral blood of the patient, whereas it was low or undetectable in control lines. It was therefore concluded that specific IgE responses in the patient were most likely to be mediated by Syk-dependent TCR-signalling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of T-cell antigen receptor signalling by Syk tyrosine protein kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Aug;17(8):4434-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.8.4434. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9234701 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell receptor-induced phosphorylation of the zeta chain is efficiently promoted by ZAP-70 but not Syk.Blood. 2004 Aug 1;104(3):760-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-12-4314. Epub 2004 Apr 1. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15059847
-
ZAP-70 and p72syk are signaling response elements through MHC class II molecules.Tissue Antigens. 1995 Sep;46(3 ( Pt 1)):145-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1995.tb03113.x. Tissue Antigens. 1995. PMID: 8525473
-
The Syk/ZAP-70 protein tyrosine kinase connection to antigen receptor signalling processes.Semin Immunol. 1995 Aug;7(4):227-36. doi: 10.1006/smim.1995.0027. Semin Immunol. 1995. PMID: 8520027 Review.
-
Adaptors and molecular scaffolds in immune cell signaling.Cell. 1999 Jan 8;96(1):5-8. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80953-8. Cell. 1999. PMID: 9989491 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
ZAP-70: an essential kinase in T-cell signaling.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 May;2(5):a002279. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002279. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20452964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of glycogen phosphorylation induces changes in cellular proteome and signaling pathways in MIA pancreatic cancer cells.Pancreas. 2012 Apr;41(3):397-408. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318236f022. Pancreas. 2012. PMID: 22158071 Free PMC article.
-
ZAP70: a master regulator of adaptive immunity.Semin Immunopathol. 2010 Jun;32(2):107-16. doi: 10.1007/s00281-010-0196-x. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Semin Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 20135127 Review.
-
Congenital disease SNPs target lineage specific structural elements in protein kinases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jul 1;105(26):9011-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802403105. Epub 2008 Jun 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18579784 Free PMC article.
-
Morpholino-based correction of hypomorphic ZAP70 mutation in an adult with combined immunodeficiency.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 May;139(5):1688-1692.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.02.002. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28216435 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Elder ME, Lin D, Clever J, Chan AC, Hope TJ, Weiss A, Parslow TG. Human severe combined immunodeficiency due to a defect in ZAP-70, a T cell tyrosine kinase. Science. 1994;264:1596–9. - PubMed
-
- Arpaia E, Shahar M, Dadi H, Cohen A, Roifman CM. Defective T cell receptor signaling and CD8+ thymic selection in humans lacking zap-70 kinase. Cell. 1994;76:947–58. - PubMed
-
- Chan AC, Kadlecek TA, Elder ME, Filipovich AH, Kuo WL, Iwashima M, Parslow TG, Weiss A. ZAP-70 deficiency in an autosomal recessive form of severe combined immunodeficiency. Science. 1994;264:1599–601. - PubMed
-
- Elder ME, Hope TJ, Parslow TG, Umetsu DT, Wara DW, Cowan MJ. Severe combined immunodeficiency with absence of peripheral blood CD8+ T cells due to ZAP-70 deficiency. Cell Immunol. 1995;165:110–7. 10.1006/cimm.1995.1193. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

