Biochemical and X-ray crystallographic studies on shikimate kinase: the important structural role of the P-loop lysine
- PMID: 11369852
- PMCID: PMC2374015
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.52501
Biochemical and X-ray crystallographic studies on shikimate kinase: the important structural role of the P-loop lysine
Abstract
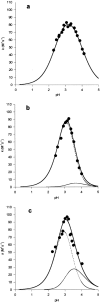
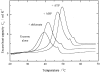
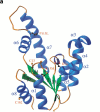
Shikimate kinase, despite low sequence identity, has been shown to be structurally a member of the nucleoside monophosphate (NMP) kinase family, which includes adenylate kinase. In this paper we have explored the roles of residues in the P-loop of shikimate kinase, which forms the binding site for nucleotides and is one of the most conserved structural features in proteins. In common with many members of the P-loop family, shikimate kinase contains a cysteine residue 2 amino acids upstream of the essential lysine residue; the side chains of these residues are shown to form an ion pair. The C13S mutant of shikimate kinase was found to be enzymatically active, whereas the K15M mutant was inactive. However, the latter mutant had both increased thermostability and affinity for ATP when compared to the wild-type enzyme. The structure of the K15M mutant protein has been determined at 1.8 A, and shows that the organization of the P-loop and flanking regions is heavily disturbed. This indicates that, besides its role in catalysis, the P-loop lysine also has an important structural role. The structure of the K15M mutant also reveals that the formation of an additional arginine/aspartate ion pair is the most likely reason for its increased thermostability. From studies of ligand binding it appears that, like adenylate kinase, shikimate kinase binds substrates randomly and in a synergistic fashion, indicating that the two enzymes have similar catalytic mechanisms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of shikimate kinase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals the dynamic role of the LID domain in catalysis.J Mol Biol. 2002 Jun 7;319(3):779-89. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00339-X. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12054870
-
Conformational changes during the catalytic cycle of gluconate kinase as revealed by X-ray crystallography.J Mol Biol. 2002 May 10;318(4):1057-69. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00215-2. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12054802
-
Catalytic independent functions of a protein kinase as revealed by a kinase-dead mutant: study of the Lys72His mutant of cAMP-dependent kinase.J Mol Biol. 2005 Sep 2;351(5):1110-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.06.011. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16054648
-
The three-dimensional structure of shikimate kinase.J Mol Biol. 1998 May 22;278(5):983-97. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1755. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9600856
-
Shikimate kinase, a protein target for drug design.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(5):592-604. doi: 10.2174/09298673113206660299. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24164195 Review.
Cited by
-
SCMBYK: prediction and characterization of bacterial tyrosine-kinases based on propensity scores of dipeptides.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Dec 22;17(Suppl 19):514. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1371-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 28155663 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of Helicobacter pylori shikimate kinase reveal a selective inhibitor-induced-fit mechanism.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33481. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033481. Epub 2012 Mar 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22438938 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Mycobacterium tuberculosis Shikimate Kinase Inhibitors as Potential Antibacterials.Perspect Medicin Chem. 2015 Mar 15;7:9-20. doi: 10.4137/PMC.S13212. eCollection 2015. Perspect Medicin Chem. 2015. PMID: 25861218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for the regulation mechanism of the tyrosine kinase CapB from Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS Biol. 2008 Jun 10;6(6):e143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060143. PLoS Biol. 2008. PMID: 18547145 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of Staphylococcus aureus cytidine monophosphate kinase in complex with cytidine 5'-monophosphate.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2006 Aug 1;62(Pt 8):710-5. doi: 10.1107/S174430910602447X. Epub 2006 Jul 24. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2006. PMID: 16880539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birkett, D.J., Price, N.C., Radda, G.K., and Salmon, A.G. 1970. The reactivity of SH groups with a fluorogenic reagent. FEBS Lett. 6 346–348. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72 255–260. - PubMed
-
- Brocklehurst, K. 1982. Two-protonic-state electrophiles as probes of enzyme mechanism. Methods Enzymol. 87C 427–469. - PubMed
-
- ———. 1994. A sound basis for pH-dependent kinetic studies on enzymes. Protein Eng. 7 291–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

