Mapping of contact sites in complex formation between transducin and light-activated rhodopsin by covalent crosslinking: use of a photoactivatable reagent
- PMID: 11320237
- PMCID: PMC33131
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.051632898
Mapping of contact sites in complex formation between transducin and light-activated rhodopsin by covalent crosslinking: use of a photoactivatable reagent
Abstract
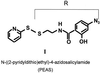
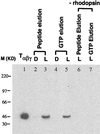
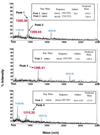
Interaction of light-activated rhodopsin with transducin (T) is the first event in visual signal transduction. We use covalent crosslinking approaches to map the contact sites in interaction between the two proteins. Here we use a photoactivatable reagent, N-[(2-pyridyldithio)-ethyl], 4-azido salicylamide. The reagent is attached to the SH group of cytoplasmic monocysteine rhodopsin mutants by a disulfide-exchange reaction with the pyridylthio group, and the derivatized rhodopsin then is complexed with T by illumination at lambda >495 nm. Subsequent irradiation of the complex at lambda310 nm generates covalent crosslinks between the two proteins. Crosslinking was demonstrated between T and a number of single cysteine rhodopsin mutants. However, sites of crosslinks were investigated in detail only between T and the rhodopsin mutant S240C (cytoplasmic loop V-VI). Crosslinking occurred predominantly with T(alpha). For identification of the sites of crosslinks in T(alpha), the strategy used involved: (i) derivatization of all of the free cysteines in the crosslinked proteins with N-ethylmaleimide; (ii) reduction of the disulfide bond linking the two proteins and isolation of all of the T(alpha) species carrying the crosslinked moiety with a free SH group; (iii) adduct formation of the latter with the N-maleimide moiety of the reagent, maleimido-butyryl-biocytin, containing a biotinyl group; (iv) trypsin degradation of the resulting T(alpha) derivatives and isolation of T(alpha) peptides carrying maleimido-butyryl-biocytin by avidin-agarose chromatography; and (v) identification of the isolated peptides by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. We found that crosslinking occurred mainly to two C-terminal peptides in T(alpha) containing the amino acid sequences 310-313 and 342-345.
Figures


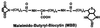
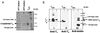

Comment in
-
How activated receptors couple to G proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):4819-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.011099798. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11320227 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Mapping of contact sites in complex formation between light-activated rhodopsin and transducin by covalent crosslinking: use of a chemically preactivated reagent.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):4883-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.051632998. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11320238 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function in rhodopsin: covalent crosslinking of the rhodopsin (metarhodopsin II)-transducin complex--the rhodopsin cytoplasmic face links to the transducin alpha subunit.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7643-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7643. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 8052635 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cysteine substitution mutants at amino acid positions 306-321 in rhodopsin, the sequence between the cytoplasmic end of helix VII and the palmitoylation sites: sulfhydryl reactivity and transducin activation reveal a tertiary structure.Biochemistry. 1999 Jun 22;38(25):7925-30. doi: 10.1021/bi9900119. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10387034
-
Interaction of rhodopsin with the G-protein, transducin.Bioessays. 1993 Jan;15(1):43-50. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150107. Bioessays. 1993. PMID: 8466475 Review.
-
Mechanism of G-protein activation by rhodopsin.Photochem Photobiol. 2007 Jan-Feb;83(1):70-5. doi: 10.1562/2006-03-22-IR-854. Photochem Photobiol. 2007. PMID: 16800722 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating mass spectrometry of intact protein complexes into structural proteomics.Proteomics. 2012 May;12(10):1547-64. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100520. Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22611037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CLPM: a cross-linked peptide mapping algorithm for mass spectrometric analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Jul 15;6 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-S2-S9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16026606 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodopsin-transducin interface: studies with conformationally constrained peptides.Biophys J. 2001 Dec;81(6):3285-93. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75962-0. Biophys J. 2001. PMID: 11720992 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical modifications of respiratory complex I for structural and functional studies.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2014 Aug;46(4):313-21. doi: 10.1007/s10863-014-9562-z. Epub 2014 Jul 4. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2014. PMID: 24993592 Review.
-
Synthesis of biotin-tagged chemical cross-linkers and their applications for mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2009 Jun;23(11):1719-26. doi: 10.1002/rcm.4066. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2009. PMID: 19412923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khorana H G. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Franke R H, Sakmar T P, Graham R M, Khorana H G. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:14767–14774. - PubMed
-
- Yang K, Farrens D L, Hubbell W L, Khorana H G. Biochemistry. 1996;35:12464–12469. - PubMed
-
- Cai K, Klein-Seetharaman J, Farrens D, Cheng Z, Altenbach C A, Hubbell W L, Khorana H G. Biochemistry. 1999;38:7925–7930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

