Shwachman-Diamond syndrome with exocrine pancreatic dysfunction and bone marrow failure maps to the centromeric region of chromosome 7
- PMID: 11254457
- PMCID: PMC1275624
- DOI: 10.1086/319505
Shwachman-Diamond syndrome with exocrine pancreatic dysfunction and bone marrow failure maps to the centromeric region of chromosome 7
Abstract
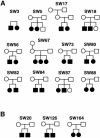
Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and hematologic and skeletal abnormalities. A genomewide scan of families with SDS was terminated at approximately 50% completion, with the identification of chromosome 7 markers that showed linkage with the disease. Finer mapping revealed significant linkage across a broad interval that included the centromere. The maximum two-point LOD score was 8.7, with D7S473, at a recombination fraction of 0. The maximum multipoint LOD score was 10, in the interval between D7S499 and D7S482 (5.4 cM on the female map and 0 cM on the male map), a region delimited by recombinant events detected in affected children. Evidence from all 15 of the multiplex families analyzed provided support for the linkage, consistent with a single locus for SDS. However, the presence of several different mutations is suggested by the heterogeneity of disease-associated haplotypes in the candidate region.
Figures
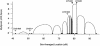
Similar articles
-
Fine mapping of the locus for Shwachman-Diamond syndrome at 7q11, identification of shared disease haplotypes, and exclusion of TPST1 as a candidate gene.Eur J Hum Genet. 2002 Apr;10(4):250-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200798. Eur J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 12032733
-
[Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. A case report].An Pediatr (Barc). 2006 Jul;65(1):79-82. doi: 10.1157/13090901. An Pediatr (Barc). 2006. PMID: 16945294 Spanish.
-
Acquired copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 7 associated with clonal haematopoiesis in a patient with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Br J Haematol. 2012 Nov;159(4):480-2. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12032. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Br J Haematol. 2012. PMID: 22934832 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
[Two cases of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome with genetic confirmation and literature review].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Sep;51(9):679-83. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24330988 Review. Chinese.
-
Diagnosis, Treatment, and Molecular Pathology of Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2018 Aug;32(4):687-700. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2018.04.006. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2018. PMID: 30047420 Review.
Cited by
-
Sixth International Congress on Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: from patients to genes and back.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Dec;1242:26-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06348.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 22191554 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical spectrum and molecular pathophysiology of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.Curr Opin Hematol. 2011 Jan;18(1):30-5. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e32834114a5. Curr Opin Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21124213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutropenia in Childhood-A Narrative Review and Practical Diagnostic Approach.Hematol Rep. 2024 Jun 16;16(2):375-389. doi: 10.3390/hematolrep16020038. Hematol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38921186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonsense Suppression Therapy: New Hypothesis for the Treatment of Inherited Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 30;21(13):4672. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134672. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between Sdo1p and Btn1p in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae model for Batten disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Mar 1;19(5):931-42. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp560. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20015955 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for genetic maps)
-
- Genetic Location Database, The, http://cedar.genetics.soton.ac.uk/public_html/ldb.html (for map locations on chromosome 7)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for SDS [MIM 260400]) - PubMed
-
- Stanford Human Genome Center (SHGC) Web, http://www-shgc.stanford.edu/ (for G3 radiation hybrid map, version 2.0)
References
-
- Bodian M, Sheldon W, Lightwood R (1964) Congenital hypoplasia of the exocrine pancreas. Acta Paediatr 53:282–293 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

