Somatic and germline mosaic mutations in the doublecortin gene are associated with variable phenotypes
- PMID: 10915612
- PMCID: PMC1287517
- DOI: 10.1086/303043
Somatic and germline mosaic mutations in the doublecortin gene are associated with variable phenotypes
Abstract
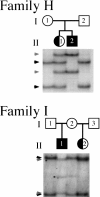
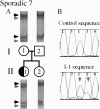
Mutations in the X-linked gene doublecortin lead to "double cortex" syndrome (DC) in females and to X-linked lissencephaly (XLIS) in males. Because most patients with DC and XLIS are sporadic, representing de novo doublecortin mutations, we considered that some of these patients could be somatic or germline mosaics. Among a population of 20 patients and their families, we found evidence for mosaic doublecortin mutations in 6 individuals. Germline mosaicism was identified in two unaffected women, each with two affected children. Additionally, one affected male with DC was found to be a somatic mosaic, which presumably spared him from the more severe phenotype of lissencephaly. The high rate of mosaicism indicates that there may be a significant recurrence risk for DC/XLIS in families at risk, even when the mother is unaffected.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Somatic mosaicism and variable penetrance in doublecortin-associated migration disorders.Neurology. 2003 Jan 28;60(2):329-32. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000042091.90361.d2. Neurology. 2003. PMID: 12552055
-
A novel DCX missense mutation in a family with X-linked lissencephaly and subcortical band heterotopia syndrome inherited from a low-level somatic mosaic mother: Genetic and functional studies.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2016 Sep;20(5):788-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 30. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27292316
-
Mutation analysis of the DCX gene and genotype/phenotype correlation in subcortical band heterotopia.Eur J Hum Genet. 2001 Jan;9(1):5-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200548. Eur J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11175293
-
Epileptogenic brain malformations: clinical presentation, malformative patterns and indications for genetic testing.Seizure. 2002 Apr;11 Suppl A:532-43; quiz 544-7. Seizure. 2002. PMID: 12185771 Review.
-
Epileptogenic brain malformations: clinical presentation, malformative patterns and indications for genetic testing.Seizure. 2001 Oct;10(7):532-43; quiz 544-7. doi: 10.1053/seiz.2001.0650. Seizure. 2001. PMID: 11749114 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Basis of Brain Malformations.Mol Syndromol. 2016 Sep;7(4):220-233. doi: 10.1159/000448639. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Mol Syndromol. 2016. PMID: 27781032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A roadmap for precision medicine in the epilepsies.Lancet Neurol. 2015 Dec;14(12):1219-28. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00199-4. Epub 2015 Sep 20. Lancet Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26416172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain Somatic Mutation in Aging and Alzheimer's Disease.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2021 Aug 31;22:239-256. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-121520-081242. Epub 2021 May 12. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33979534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mosaic DCX deletion causes subcortical band heterotopia in males.Neurogenetics. 2012 Nov;13(4):367-73. doi: 10.1007/s10048-012-0339-4. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Neurogenetics. 2012. PMID: 22833188
-
Single-cell, genome-wide sequencing identifies clonal somatic copy-number variation in the human brain.Cell Rep. 2014 Sep 11;8(5):1280-9. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.043. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25159146 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for DC [MIM 600348 and MIM 300067], XLIS [MIM 300067], DCX [MIM 300121], and LIS1 [MIM 247200])
References
-
- Alvarado M, Bass HN, Caldwell S, Jamehdor M, Miller AA, Jacob P (1993) Miller-Dieker syndrome: detection of a cryptic chromosome translocation using in situ hybridization in a family with multiple affected offspring. Am J Dis Child 147:1291–1294 - PubMed
-
- Berg MJ, Schifitto G, Powers JM, Martinez-Capolino C, Fong CT, Myers GJ, Epstein LG, Walsh CA (1998) X-linked female band heterotopia-male lissencephaly syndrome. Neurology 50:1143–1146 - PubMed
-
- Clark GD, Noebels JL (1999) Cortin disaster: lissencephaly genes spell double trouble for the developing brain. Ann Neurol 45:141–142 - PubMed
-
- des Portes V, Francis F, Pinard JM, Desguerre I, Moutard ML, Snoeck I, Meiners LC, Capron F, Cusmai R, Ricci S, Motte J, Echenne B, Ponsot G, Dulac O, Chelly J, Beldjord C (1998a) doublecortin is the major gene causing X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia (SCLH). Hum Mol Genet 7:1063–1070 - PubMed
-
- des Portes V, Pinard JM, Billuart P, Vinet MC, Koulakoff A, Carrie A, Gelot A, Dupuis E, Motte J, Berwald-Netter Y, Catala M, Kahn A, Beldjord C, Chelly J (1998b) A novel CNS gene required for neuronal migration and involved in X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia and lissencephaly syndrome. Cell 92:51–61 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

