PNG1, a yeast gene encoding a highly conserved peptide:N-glycanase
- PMID: 10831608
- PMCID: PMC2174826
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.5.1039
PNG1, a yeast gene encoding a highly conserved peptide:N-glycanase
Abstract
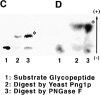
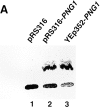
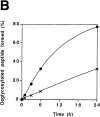
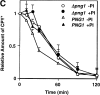
It has been proposed that cytoplasmic peptide:N-glycanase (PNGase) may be involved in the proteasome-dependent quality control machinery used to degrade newly synthesized glycoproteins that do not correctly fold in the ER. However, a lack of information about the structure of the enzyme has limited our ability to obtain insight into its precise biological function. A PNGase-defective mutant (png1-1) was identified by screening a collection of mutagenized strains for the absence of PNGase activity in cell extracts. The PNG1 gene was mapped to the left arm of chromosome XVI by genetic approaches and its open reading frame was identified. PNG1 encodes a soluble protein that, when expressed in Escherichia coli, exhibited PNGase activity. PNG1 may be required for efficient proteasome-mediated degradation of a misfolded glycoprotein. Subcellular localization studies indicate that Png1p is present in the nucleus as well as the cytosol. Sequencing of expressed sequence tag clones revealed that Png1p is highly conserved in a wide variety of eukaryotes including mammals, suggesting that the enzyme has an important function.
Figures


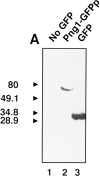
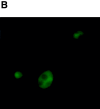


Similar articles
-
Identification of proteins that interact with mammalian peptide:N-glycanase and implicate this hydrolase in the proteasome-dependent pathway for protein degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Sep 25;98(20):11163-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.201393498. Epub 2001 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11562482 Free PMC article.
-
A role for N-glycanase in the cytosolic turnover of glycoproteins.EMBO J. 2003 Mar 3;22(5):1036-46. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg107. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12606569 Free PMC article.
-
The PUB domain: a putative protein-protein interaction domain implicated in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Oct 12;287(5):1083-7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5688. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11587532
-
Cytoplasmic peptide:N-glycanase (PNGase) in eukaryotic cells: occurrence, primary structure, and potential functions.FASEB J. 2002 May;16(7):635-41. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0889rev. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 11978727 Review.
-
Physiological and molecular functions of the cytosolic peptide:N-glycanase.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 May;41:110-20. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.11.009. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25475175 Review.
Cited by
-
The evolution of N-glycan-dependent endoplasmic reticulum quality control factors for glycoprotein folding and degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 10;104(28):11676-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704862104. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17606910 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of proteins that interact with mammalian peptide:N-glycanase and implicate this hydrolase in the proteasome-dependent pathway for protein degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Sep 25;98(20):11163-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.201393498. Epub 2001 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11562482 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic O-GlcNAcylation and PNG1 maintain Drosophila gut homeostasis by regulating proliferation and apoptosis.PLoS Genet. 2022 Mar 16;18(3):e1010128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010128. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35294432 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol deacylation by Bst1p is required for the quality control of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Feb;17(2):834-50. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-05-0443. Epub 2005 Nov 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16319176 Free PMC article.
-
The Neurospora peptide:N-glycanase ortholog PNG1 is essential for cell polarity despite its lack of enzymatic activity.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 22;285(4):2326-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.045302. Epub 2009 Nov 25. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19940117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bebök Z., Mazzochi C., King S.A., Hong J.S., Sorscher E.J. The mechanism underlying cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the proteasome includes Sec61β and a cytosolic, deglycosylated intermediary. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:29873–29878. - PubMed
-
- Berger S., Menudier A., Julien R., Karamanos Y. Do de-N-glycosylation enzymes have an important role in plant cells? Biochimie. 1995;77:751–760. - PubMed
-
- Brodsky J.L., McCracken A.A. ER protein quality control and proteasome-mediated protein degradation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999;10:507–513. - PubMed
-
- Cresswell P., Hughes E.A. Protein degradationthe ins and outs of the matter. Curr. Biol. 1997;7:R552–R555. - PubMed
-
- de Virgilio M., Weninger H., Ivessa N.E. Ubiquitination is required for the retro-translocation of a short-lived luminal endoplasmic reticulum glycoprotein to the cytosol for degradation by the proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:9734–9743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

