Identification of filamin as a novel ligand for caveolin-1: evidence for the organization of caveolin-1-associated membrane domains by the actin cytoskeleton
- PMID: 10637311
- PMCID: PMC14777
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.11.1.325
Identification of filamin as a novel ligand for caveolin-1: evidence for the organization of caveolin-1-associated membrane domains by the actin cytoskeleton
Abstract
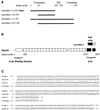
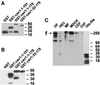
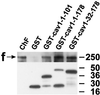
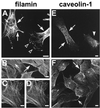
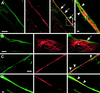
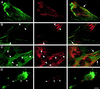
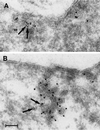
Reports on the ultrastructure of cells as well as biochemical data have, for several years, been indicating a connection between caveolae and the actin cytoskeleton. Here, using a yeast two-hybrid approach, we have identified the F-actin cross-linking protein filamin as a ligand for the caveolae-associated protein caveolin-1. Binding of caveolin-1 to filamin involved the N-terminal region of caveolin-1 and the C terminus of filamin close to the filamin-dimerization domain. In in vitro binding assays, recombinant caveolin-1 bound to both nonmuscle and muscle filamin, indicating that the interaction might not be cell type specific. With the use of confocal microscopy, colocalization of caveolin-1 and filamin was observed in elongated patches at the plasma membrane. Remarkably, when stress fiber formation was induced with Rho-stimulating Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1, the caveolin-1-positive structures became coaligned with stress fibers, indicating that there was a physical link connecting them. Immunogold double-labeling electron microscopy confirmed that caveolin-1-labeled racemose caveolae clusters were positive for filamin. The actin network, therefore, seems to be directly involved in the spatial organization of caveolin-1-associated membrane domains.
Figures

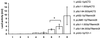
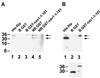
Similar articles
-
Filamin A regulates caveolae internalization and trafficking in endothelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Nov;20(21):4531-40. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-10-0997. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19759182 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubules and actin microfilaments regulate lipid raft/caveolae localization of adenylyl cyclase signaling components.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 8;281(36):26391-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602577200. Epub 2006 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16818493
-
Filamin A is a novel caveolin-1-dependent target in IGF-I-stimulated cancer cell migration.Exp Cell Res. 2008 Sep 10;314(15):2762-73. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.06.004. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Exp Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18598695
-
Mechanical response of single filamin A (ABP-280) molecules and its role in the actin cytoskeleton.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002;23(5-6):525-34. doi: 10.1023/a:1023418725001. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002. PMID: 12785102 Review.
-
Structural and functional aspects of filamins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Apr 23;1538(2-3):99-117. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(01)00072-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. PMID: 11336782 Review.
Cited by
-
Time-resolved proximity proteomics uncovers a membrane tension-sensitive caveolin-1 interactome at the rear of migrating cells.Elife. 2024 Sep 24;13:e85601. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85601. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39315773 Free PMC article.
-
UTP controls cell surface distribution and vasomotor activity of the human P2Y2 receptor through an epidermal growth factor receptor-transregulated mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 29;285(5):2940-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.081166. Epub 2009 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19996104 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation-dependence of caveolae-mediated endocytosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2007 Nov-Dec;11(6):1239-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00127.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 18205698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of PTRF in PC-3 Cells modulates cholesterol dynamics and the actin cytoskeleton impacting secretion pathways.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Feb;11(2):M111.012245. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.012245. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22030351 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytic crosstalk: cavins, caveolins, and caveolae regulate clathrin-independent endocytosis.PLoS Biol. 2014 Apr 8;12(4):e1001832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001832. eCollection 2014 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2014. PMID: 24714042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aktories K. Rho proteins: targets for bacterial toxins. Trends Microbiol. 1997;5:282–288. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RG. The caveolae membrane system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:199–225. - PubMed
-
- Couet J, Li S, Okamoto T, Ikezu T, Lisanti MP. Identification of peptide and protein ligands for the caveolin-scaffolding domain: implications for the interaction of caveolin with caveolae-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:6525–6533. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham CC, Gorlin JB, Kwiatkowski DJ, Hartwig JH, Janmey PA, Byers HR, Stossel TP. Actin-binding protein requirement for cortical stability and efficient locomotion. Science. 1992;255:325–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

