Clustered 11q23 and 22q11 breakpoints and 3:1 meiotic malsegregation in multiple unrelated t(11;22) families
- PMID: 10577913
- PMCID: PMC1288370
- DOI: 10.1086/302666
Clustered 11q23 and 22q11 breakpoints and 3:1 meiotic malsegregation in multiple unrelated t(11;22) families
Abstract
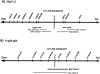
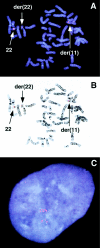
The t(11;22) is the only known recurrent, non-Robertsonian constitutional translocation. We have analyzed t(11;22) balanced-translocation carriers from multiple unrelated families by FISH, to localize the t(11;22) breakpoints on both chromosome 11 and chromosome 22. In 23 unrelated balanced-translocation carriers, the breakpoint was localized within a 400-kb interval between D22S788 (N41) and ZNF74, on 22q11. Also, 13 of these 23 carriers were tested with probes from chromosome 11, and, in each, the breakpoint was localized between D11S1340 and APOA1, on 11q23, to a region </=185 kb. Thus, the breakpoints on both chromosome 11 and chromosome 22 are clustered in multiple unrelated families. Supernumerary-der(22)t(11;22) syndrome can occur in the progeny of balanced-t(11;22) carriers, because of malsegregation of the der(22). There has been speculation regarding the mechanism by which the malsegregation occurs. To elucidate this mechanism, we have analyzed 16 of the t(11;22) families, using short tandem-repeat-polymorphism markers on both chromosome 11 and chromosome 22. In all informative cases the proband received two of three alleles, for markers above the breakpoint on chromosome 22 and below the breakpoint on chromosome 11, from the t(11;22)-carrier parent. These data strongly suggest that 3:1 meiosis I malsegregation in the t(11;22) balanced-translocation-carrier parent is the mechanism in all 16 families. Taken together, these results establish that the majority of t(11;22) translocations occur within the same genomic intervals and that the majority of supernumerary-der(22) offspring result from a 3:1 meiosis I malsegregation in the balanced-translocation carrier.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tightly clustered 11q23 and 22q11 breakpoints permit PCR-based detection of the recurrent constitutional t(11;22).Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Sep;67(3):763-8. doi: 10.1086/303054. Epub 2000 Jul 20. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10903930 Free PMC article.
-
A common breakpoint on 11q23 in carriers of the constitutional t(11;22) translocation.Am J Hum Genet. 1999 Dec;65(6):1608-16. doi: 10.1086/302689. Am J Hum Genet. 1999. PMID: 10577914 Free PMC article.
-
AT-rich palindromes mediate the constitutional t(11;22) translocation.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Jan;68(1):1-13. doi: 10.1086/316952. Epub 2000 Nov 28. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11095996 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic disorders on 22q11.Am J Hum Genet. 2002 May;70(5):1077-88. doi: 10.1086/340363. Epub 2002 Mar 29. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11925570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Identification of the breakpoint-flanking markers on chromosomes 1 and 17 of a constitutional translocation T(1;17)(P36;Q12-21) in a patient with neuroblastoma].Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1995;57(5):389-422. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1995. PMID: 8571670 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Meiotic studies of a human male carrier of the common translocation, t(11;22), suggests postzygotic selection rather than preferential 3:1 MI segregation as the cause of liveborn offspring with an unbalanced translocation.Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Sep;67(3):601-9. doi: 10.1086/303052. Epub 2000 Aug 8. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10936106 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic recombination and spatial proximity in the etiology of the recurrent t(11;22).Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Sep;79(3):524-38. doi: 10.1086/507652. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Am J Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16909390 Free PMC article.
-
XX male with sex reversal and a de novo 11;22 translocation.Am J Med Genet A. 2006 Sep 15;140(18):1973-7. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31397. Am J Med Genet A. 2006. PMID: 16894539 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Tightly clustered 11q23 and 22q11 breakpoints permit PCR-based detection of the recurrent constitutional t(11;22).Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Sep;67(3):763-8. doi: 10.1086/303054. Epub 2000 Jul 20. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10903930 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal cfDNA Screening for Emanuel Syndrome and Other Unbalanced Products of Conception in Carriers of the Recurrent Balanced Translocation t(11;22): One Laboratory's Retrospective Experience.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 10;14(10):1924. doi: 10.3390/genes14101924. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895273 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- NCBI GenBank Overview, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/GenbankOverview.html (for searches of the BLAST Database and for APOAI cDNA [accession number J00098], PAC 201m18 [accession number AC000097], and BAC 422e11 [BAC b1030 in ; accession number AC007707])
-
- University of Oklahoma Advanced Center for Genome Technology http://dna1.chem.ou.edu/index.html (for maps of 22q11 and sequences of clones from 22q11.2)
References
-
- Abeliovich D, Carmi R (1990) The translocation 11q;22q: a novel unbalanced karyotype. Am J Med Genet. 37:288 - PubMed
-
- Arai Y, Hosoda F, Nakayama K, Ohki M (1996) A yeast artificial chromosome contig and NotI restriction map that spans the tumor suppressor gene(s) locus, 11q22.2 -q23.3. Genomics 35:196–206 - PubMed
-
- Aurias A, Rimbaut C, Buffe D, Zucker JM, Mazabraud A (1984) Translocation involving chromosome 22 in Ewing's sarcoma: a cytogenetic study of four fresh tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 12(1): 21–25 - PubMed
-
- Budarf ML, Emanuel BS (1997) Progress in autosomal segmental aneusomy syndromes (SASs): single or multi-locus disorders? Hum Mol Genet 6:1657–1665 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

